What is Myopathy? Myopathy is a disease that occurs due to a disturbance in the metabolism and structure of muscle tissue, as a result of which a decrease in the strength of the affected muscles appears and a limitation of motor activity.
Myopathies belong to the group of neuromuscular diseases, characterized by dystrophic lesions of muscle tissue with atrophy of individual fibers (myofibrils) in some places. In addition, the atrophied myofibrils are replaced by connective or adipose tissue; this leads to the loss of the ability of the muscles to contract, which leads to the appearance in the clinic of the disease of muscle weakness and the limitation of motor activity.
There are two main forms of myopathy:
- Primary myopathies, which are often hereditary. In turn, they are divided into the following types:
- congenital myopathies that develop during infancy
- early childhood myopathies that develop at the age of 5-10 years
- juvenile myopathies that develop during adolescence.
- Secondary myopathies are arising from the background of other diseases.
For example, against the background of endocrine disorders (Itsenko-Cushing’s disease, hyperaldosteronism, hyperparathyroidism, hypo-, and hyperthyroidism), chronic intoxications (alcoholism, drug addiction, work at enterprises with occupational hazards), severe chronic diseases (chronic renal failure, chronic liver failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, heart failure), and tumor processes.
Primary forms of myopathy are much more common than secondary ones. Therefore, it is essential during pregnancy planning to consult a geneticist to identify the risk of developing this pathology in an unborn child.
Based on which part of the body muscle weakness is more pronounced, the following types of myopathy are distinguished:
- the proximal pathological process is located in those parts of the limbs that are as close as possible to the body (for example, in the case of the arms, these are the shoulders)
- the distal muscles of the limbs are affected, which are at maximum distance from the body (for example, in the case of the legs, the calf muscles)
- mixed has symptoms of proximal and distal forms of the disease.
Primary myopathies have a poor prognosis, especially if the first symptoms appeared in early childhood. The involvement of the heart muscle and respiratory muscles in the process is also essential. In this case, the prognosis of the disease worsens. The most favorable outcome is observed in secondary myopathies since, in this case, it is easier to achieve success in the treatment of the underlying disease that caused the development of myopathy.
Diagnosis of myopathy
The doctor may suspect the presence of myopathy even at the level of the initial examination since an appropriate appearance characterizes such people.
- First, there is muscle atrophy (proximal extremities) and pseudohypertrophy of the distal extremities.
- Secondly, over time, a duck gait is formed. Also, myopathy is characterized by drooping of the shoulders, pterygoid lagging of the shoulder blades, protrusion of the abdomen forward, and increased lumbar lordosis.
Then the doctor proceeds to a neurological examination, during which he reveals a weakening of tendon reflexes, a decrease in muscle strength. Unlike neuropathy, myopathy does not impair sensitivity.
After the examination, the patient is sent to the laboratory to pass the required list of tests. One of these is urinalysis, which looks for creatinine to confirm myopathy. The presence of creatinine in the urine may indicate muscle damage; therefore, this indicator is not devoid of informative value in diagnosing the disease in question. Next, a biochemical blood test is performed, in which the level of enzymes is assessed.
In addition, electrophysiological research methods are used in electroneurography and electromyography.
- The results of electroneurography provide information about the state of the peripheral motor neuron, which is necessary if there is a suspicion of neuropathy.
- Electromyography is performed to assess the condition of muscle tissue directly. With myopathy, there is a change in muscle potentials (their amplitude decreases and their duration decreases).
The most informative method is a morphological examination of muscle tissue; this is done with a muscle biopsy. Although the most informative, this method is rarely carried out, only in cases where the previous research methods did not provide adequate information to confirm a particular diagnosis. In myopathy, the morphological picture of muscle tissue samples is as follows: randomly scattered atrophied myofibrils (contractile elements of muscle fibers), hypertrophied muscle fibers, and replacement of muscle tissue with connective or adipose tissue is observed.
A consultation with a cardiologist is appointed; they will then send the patient for an ECG and ultrasound of the heart to assess the condition of the heart muscle. If pneumonia is suspected as a complication of the course of myopathy, an X-ray of the lungs is performed.
Treatment of myopathy
For the treatment of primary forms of myopathy, there are no drugs that can eliminate genetic defects that caused the development of the disease. In this case, treatment is only symptomatic. It aims to alleviate the symptoms of the disease and improve the quality of life.
For this purpose, anabolic hormones, anticholinesterase drugs, and vitamin complexes are prescribed. The effect of these drugs is aimed at inhibiting dystrophic and atrophic changes in muscle tissue.
Secondary forms of myopathy respond better to treatment since therapy aims to eliminate concomitant diseases that caused the development of myopathy. In the case of a competent selection of drug and non-drug methods of treatment, there is a gradual elimination of symptoms that bother people with myopathy against the background of endocrine disorders, chronic intoxication, severe chronic diseases, etc.
The appointment of physiotherapy complements the above treatment methods. For example, electrophoresis with neostigmine, iontophoresis with calcium, and ultrasound are used.
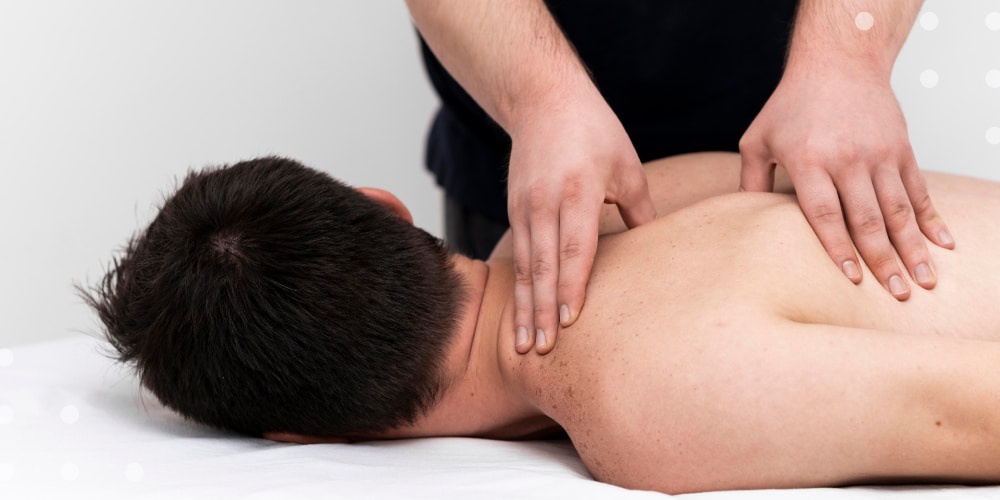
In addition, it is essential to prescribe massage and exercise therapy. The use of these treatment methods is aimed at slowing down the process of dystrophic changes in muscle tissue with subsequent atrophy. Also, due to constant physical activity, the degeneration of muscle tissue into connective and adipose tissue is reduced. However, it is essential not to overload the weakened muscles; therefore, the set of exercises is selected by a qualified specialist.
Much attention is paid to breathing exercises, which aim to improve the ventilation of the lungs; this is necessary to prevent the development of complications in the form of pneumonia, which can occur due to damage to the respiratory muscles.
Medicines to treat myopathy
The goal of myopathy treatment is to reduce muscle atrophy. Anabolic hormones (retabolil, nerobol) are of great help in this. Their action is expressed in stimulating the growth of muscle cells, which is necessary for maintaining muscle mass. Due to this, there is an increase in the indicator of strength, performance, and endurance. However, there is a downside to taking these drugs. With prolonged use, side effects may occur in the form of baldness or increased hair growth on the face and body. In addition, there is such a concept as masculinization, which means the appearance of secondary sexual characteristics of the male sex in women. In this case, there is a change in the female constitution; the voice deepens, the menstrual cycle is disrupted, the elasticity of the skin changes, and acne appears.
From anticholinesterase drugs, drugs such as proserin, neuromidin are used. Preference is given to neuromidin, as its spectrum of action is much wider than proserin. Also, with prolonged use of proserin, various unpleasant side effects are noted. Therefore, in most cases, the drug is prescribed in short courses.
In turn, neuromidin has a good stimulating effect on neuromuscular transmission and increases the contractile activity of muscles. In addition, neuromidin has sedative and analgesic (relieves pain) effects.
Vitamins of groups E, B, and C, and nicotinic acid, are used from vitamin preparations.










Please, leave your review
Write a comment: