After a stroke, the majority of people suffer from communication issues. These impairments can include slurred speech, difficulty finding the right word, or trouble organizing thoughts when speaking. Types of speech disorders include dysarthria and aphasia.
Dysarthria may make it hard to communicate clearly or softly. It can also affect the pitch, volume, or rate of speech. People with dysarthria often do not know how their speech sounds to others. Dysarthria occurs in 41% of people who have had a stroke. In half of them, it passes within three months. Some people have trouble understanding speech. This is called aphasia.
Aphasia can make it hard to read, write, or talk. People with aphasia may have trouble finding the right word, names, or numbers. They may also have issues reading or writing. Some people have both dysarthria and aphasia after a stroke. These problems can make it hard to work, take care of daily activities, or communicate with family and friends. Stay tuned for more information on different types of speech impairment and tips on recovery after a stroke.
How Strokes Affect Speech
A stroke typically affects the nerves and muscles in one side of the body leading to difficulty speaking. This can range from mild conditions with word-finding to total loss of speech. The degree depends on how much the stroke impacts the speech center in the brain.
While the severity of speech impairments varies from person to person, some common patterns emerge after a stroke:
- For some people, the facial muscles may be weak, making it difficult to form words. Others may have trouble understanding what other people say.
- Others may speak in short phrases or sentence fragments.
- Some people may search for the right word, while others may use made-up words or substitute similar words.
- Also, many individuals have trouble with rhythm and intonation and may speak in a monotone voice.
- For some people, the damage is so severe that they cannot speak.
With treatment and practice, many people are able to improve their speech and communication skills.
Treatments for Difficulty Speaking After Stroke
Treatments can include speech therapy, cognitive rehabilitation, or medications. Combining different medicines may be necessary in many cases to achieve the best possible outcome. If you or someone you know has suffered from a stroke, it is vital immediately to seek medical help to develop an individualized treatment plan best suited to your specific needs. Once the initial medical emergency has passed, there are several ways to help with speech recovery:
- Speech therapy is one of the most effective treatments for recovering speech after a stroke. A speech therapist can help you regain lost speaking skills and improve your communication skills. Other treatments for speech problems after a stroke include medication, surgery, and assistive devices.
- Medication can be used to help control any underlying conditions that may be contributing to speech difficulties. For example, medicines that improve muscle control may be prescribed.
- Surgery may be an option if the stroke has caused damage to the vocal cords.
- Assistive devices such as computerized speech synthesizers can also help improve communication.
When to See a Doctor?
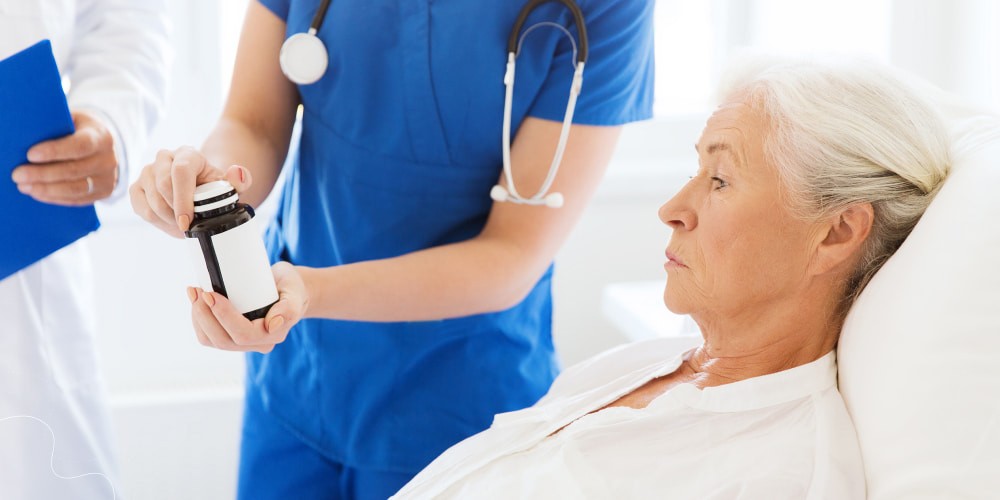
If you have difficulty speaking after a stroke, you must see a doctor as soon as possible because a stroke can cause concerns with communication and swallowing. These problems can make it difficult to eat, drink, and speak. The doctors can help you find the best way to communicate and eat. And the sooner you start treatment, the better your chances of recovery.
There are also many more reasons why it is significant to see a doctor. One reason is that the stroke may have damaged the nerves that control the muscles used for speaking. This can cause difficulty speaking or even complete loss of speech. Another reason is that the stroke may have caused damage to the brain itself, which can affect speech skills and cause difficulty speaking. Finally, strokes can also cause emotional difficulties such as anxiety and depression, making speaking difficult. In many cases, speech therapy is an effective treatment for improving speaking after a stroke. Speech therapists can help you regain the ability to speak clearly and fluently. If necessary, they can also teach you alternative communication methods, such as sign language.
Make an appointment for a consultation with Lone Star Neurology doctors
doctors
Many people have difficulty speaking after a stroke. This is because the stroke can damage the parts of the brain that control language. However, many people can improve their communication ability with the proper treatment and support. If you have difficulty speaking or want to prevent it, do not hesitate to consult with Lone Star Neurology specialists to receive the appropriate care and speech recovery after a stroke. We are always ready to provide professional and timely medical care.
FAQ
- What causes a stroke that affects speech?
Some common causes include a blockage in one of the arteries that supply blood to the brain, bleeding in the brain, or a clot that forms in another part of the body and then travels to the brain. All of these conditions can cause damage to the parts of the brain that are responsible for speech. This can lead to problems with producing or understanding speech.
- What happens when a stroke affects speech?
A stroke can cause speech difficulties, depending on which brain area is affected. A person may have trouble producing speech sounds, or they may speak in a calm voice. They may also have difficulty understanding what other people say. Some people who have had a stroke may be able to produce speech, but it may be very unclear and hard to understand.
- Can your speech be recovered after a stroke?
Yes, your speech can be recovered after a stroke. However, the extent of the recovery will depend on the severity of the stroke and the area of the brain that was affected. If the stroke was mild, you may only experience some temporary difficulty with speaking. However, if the stroke is more severe, you may experience longer-term difficulty speaking or even a complete loss of speech.
- What speech problems are common after a stroke?
Some common speech concerns after a stroke include dysarthria (difficulty speaking due to weakness or paralysis of the muscles used for speech production), aphasia (difficulty understanding or producing speech), and apraxia (difficulty executing voluntary movements). Swallowing problems are also common after a stroke.





 (1 votes, average: 4.00 out of 5)
(1 votes, average: 4.00 out of 5)




Please, leave your review
Write a comment: