There are many developmental disorders. We will discuss autism spectrum disorders (ASD). They vary widely and represent a range of neurodevelopmental features. These conditions are widespread disorders. They are typically associated with the formation of the nervous system and mental functions. Let’s delve into this topic in more detail. The condition is usually considered a broad spectrum. This happens because its manifestations vary significantly from person to person. Some individuals exhibit mild symptoms, while others experience more profound challenges. From a neurology perspective, ASD is closely linked to differences in brain development. They also appear in neural connectivity.
Understanding ASD helps provide insight. They are about the underlying causes of the disorder. They include genetic and environmental factors that may influence brain structure and function. This neurological perspective is essential. It develops more effective diagnostic tools, interventions, and support strategies. They are generally tailored to the unique needs of individuals. Let’s explore all crucial information.
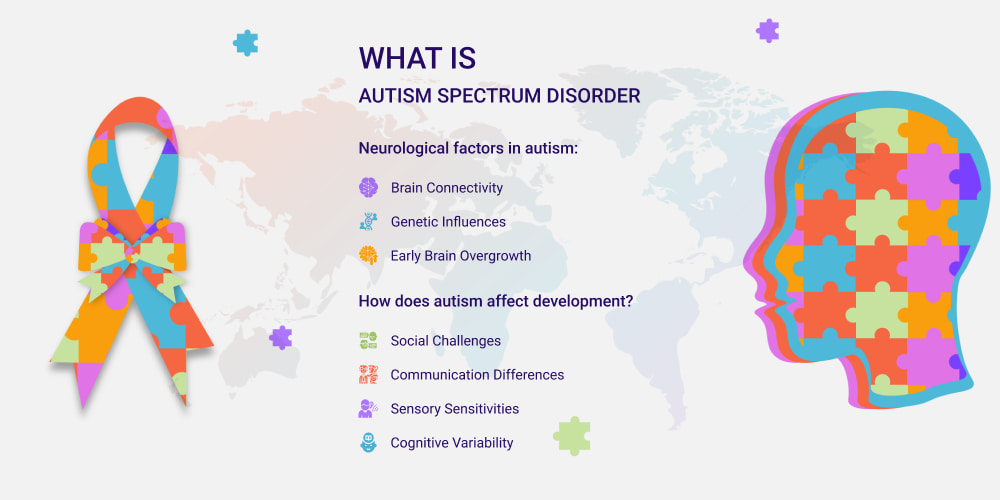
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder, and How Does it Affect Development?
ASD is a neurodevelopmental condition. It significantly impacts social interaction, communication, and behavior. This condition is typically categorized as a spectrum disorder. This means symptoms and severity vary widely among patients. Research suggests that ASD is linked to differences in brain development. They are mainly in areas related to social cognition, sensory processing, and executive function.
Let’s discuss neurological factors in autism:
- Brain Connectivity: Studies indicate atypical connections between different brain regions. They affect information processing and sensory integration.
- Genetic Influences: Variations are generally linked to altered neurological pathways and synaptic functioning.
- Early Brain Overgrowth: Some autistic individuals exhibit increased brain volume during early childhood. They affect cognitive and behavioral development.
How does autism affect development? Let’s check:
- Social Challenges: Difficulty understanding social cues, facial expressions, and conversational norms.
- Communication Differences: Some individuals may be nonverbal. Others may have advanced vocabulary but struggle with social reciprocity.
- Sensory Sensitivities: Hypersensitivity or hypersensitivity to light, sound, textures, and other stimuli.
- Cognitive Variability: Some individuals have intellectual disabilities. Others may possess exceptional skills in areas like math, music, or memory.
Understanding autism from a neurology perspective is crucial. Researchers and clinicians can develop better diagnostic tools and interventions. They will help to support individuals across the spectrum.
Neurological Foundations of Autism: What We Know So Far
Research has revealed significant differences. They appear in brain structure, connectivity, and neurotransmitter activity. These neurological variations help explain the diverse behaviors associated with ASD. They provide insights into its diagnosis and treatment:
- Brain Structure & Connectivity: Some autistic individuals experience rapid brain growth in infancy. This is mainly in the frontal and temporal lobes. They are generally involved in social processing. Research suggests that long-range connections between different brain regions may be weaker. It leads to difficulties in integrating sensory and social information. In contrast, certain short-range neural connections are overactive. They contribute to restricted interests and repetitive behaviors.
- Neurotransmitter Imbalances: Abnormal serotonin levels in the brain are linked to mood. They are also related to social behavior and sensory processing in individuals. Disruptions in excitatory (glutamate) and inhibitory (GABA) neurotransmitters affect cognitive flexibility. They also impact attention and sensory perception.
Understanding autistic disorder from a neurological perspective is crucial. Researchers are developing more precise diagnostic methods and tailored interventions. They help to support individuals across the spectrum.
Behavioral Signs and Challenges of Autism: A Neurological Insight
Distinct behavioral patterns generally characterize ASD. They stem from differences in neurological development. These behaviors reflect variations in brain connectivity, sensory processing, and neurotransmitter activity. These factors shape how individuals experience the world.
Social communication difficulties include:
- Difficulty with Verbal & Nonverbal Communication: There are challenges in speech development. They may also appear in tone modulation and eye contact. They arise from differences in the brain’s language-processing centers.
- Impaired Social Interaction: There are differences in brain regions. These are the amygdala and prefrontal cortex. Such differences affect the ability to recognize facial expressions, emotions, and social cues.
- Literal Thinking & Difficulty Understanding Nuance: The frontal lobe may process language differently. This makes interpreting sarcasm, metaphors, or implied meanings harder.
Now, let’s talk about repetitive behaviors & routines:
- Stereotyped Movements: These are hand-flapping, rocking, or repetitive speech patterns. They may be generally linked to overactive neural circuits in the motor cortex.
- Strong Preference for Routine: The basal ganglia is responsible for habit formation. It may contribute to intense resistance to change.
Sensory sensitivities also appear:
- Hypersensitivity: Overactivity in sensory-processing regions can cause extreme sensitivity. It concerns sounds, lights, and textures.
- Hyposensitivity: Some individuals may seek intense sensory input. It happens because of the reduced responses in tactile or proprioceptive brain pathways.
Understanding these characteristics through neurology is a crucial point. This understanding helps researchers develop targeted interventions. They support individuals in navigating their unique experiences.
Intervention Strategies: Neurological Approaches to Managing Autism
Early diagnosis is crucial in supporting individuals. The brain is most adaptable during early childhood. Neurologically informed therapies target brain plasticity, sensory processing, and behavioral development. They help improve communication, social skills, and overall well-being.
Let’s discuss the importance of early diagnosis:
- Enhances Brain Plasticity: Early diagnosis leverages the ability to form new neural connections. It improves social and cognitive skills.
- Supports Developmental Milestones: Addressing communication and motor skills early is crucial. It can help individuals with autism build foundational abilities.
- Reduces Severity of Symptoms: Targeted therapies can minimize sensory and behavioral challenges. They improve daily functioning.
Now, let’s talk about neurologically informed therapies:
- Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA): Uses behavioral reinforcement to encourage positive actions. Research shows its impact on neural pathways related to learning and habit formation.
- Sensory Integration Therapy: Helps individuals process sensory input more effectively. It engages neural circuits involved in touch, sound, and movement.
- Speech and Language Therapy: Strengthens neural connections in the brain’s language centers. They improve verbal and nonverbal communication.
- Occupational Therapy: Enhances motor coordination and daily skills. It utilizes brain-based approaches. This therapy helps individuals with autism support executive function and sensory regulation.
The influence of neurological research on treatment is enormous:
- Identifying Brain Differences: Advanced imaging techniques help pinpoint neurological variations. They lead to more personalized intervention plans.
- Tailored Therapies: Insights from neurology allow clinicians to develop strategies. They align with an individual’s brain function and needs.
Integrating neurology into autistic disorder intervention is essential. Researchers and clinicians can create evidence-based treatments. They improve long-term outcomes.
Advances in Neurology: Improving the Understanding and Treatment of Autism
Recent advancements have significantly improved the understanding of ASD. They lead to better diagnostic tools and innovative treatment approaches. Research in brain imaging, genetics, and neurological therapies continues. They uncover how the brain functions in individuals across the spectrum. It helps shape more effective interventions.
Let’s explore brain imaging and structural insights:
- MRI and fMRI Studies: Advanced imaging techniques reveal brain connectivity and activity differences. This is especially true in some regions. They are responsible for social interaction, sensory processing, and executive function.
- Early Detection through Neuroimaging: Identifying atypical infant brain development patterns is essential. It could enable earlier diagnosis and treatment.
- Overgrowth and Connectivity Studies: Some children on the spectrum experience early brain overgrowth. It is mainly in the frontal cortex, impacting social and communication skills.
Now, we will talk about genetic research and ASD:
- Identifying Genetic Markers: Studies have linked autism to gene variations. They affect neural growth and synaptic communication.
- Understanding Hereditary Patterns: Research indicates that genetic predisposition plays a role. Multiple genes contribute to spectrum variability.
- Gene Therapy Potential: Experimental studies important information. It explores how modifying neurological pathways at the genetic level could influence symptoms.
There are emerging treatments for neurology:
- Neurostimulation Techniques: Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) shows promise. It is generally concerned with enhancing social cognition and communication skills.
- Medication Research: Scientists are exploring drugs. They target neurotransmitter imbalances. It is particularly in serotonin, dopamine, and GABA pathways.
- Personalized Neurological Treatment: Treatments can be tailored to an individual’s neurological profile. They come with more profound insights into brain function.
Neurological research continues to advance. The potential for more precise diagnoses and effective treatments grows. It offers new hope for individuals across the autism spectrum.
The Future of Autism Spectrum Disorder Diagnosis and Treatment
Research deepens our understanding of the neurological and genetic underpinnings of ASD. Diagnostic tools are becoming more refined. They allow for earlier and more accurate identification. These developments will likely lead to a shift toward personalized interventions. Better understanding of how neural pathways typically shape behavior. Treatments can be tailored to address specific challenges. They leverage an individual’s strengths. Future therapies may include advanced strategies. They adapt to an individual’s progress in neurofeedback techniques.
Key areas of progress include:
- Early Diagnosis: This is achieved through genetic testing and brain scans.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: They are effective. Such plans are typically tailored to the specific patterns of autism.
- Advanced Neuroimaging Tools: These tools monitor progress and predict outcomes.
- Use of AI and Virtual Reality: It helps to enhance therapies.
- Broader Integration: This includes the development of community-based support systems.
These advancements promise a future where ASD diagnosis and treatment will be more effective. Through continued neurological progress, society will be better equipped to better support individuals with ASD. Neurological processes improve the quality of life and outcomes. Contact us to get a professional consultation. Our team will offer you the most effective treatment plan.







Please, leave your review
Write a comment: