Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS) is a rare autoimmune disorder affecting signals transmitted from the nerves to the muscles. The syndrome is caused by a mutation in the genes of the proteins responsible for muscle contractions. The syndrome occurs in the presence of malignant tumors (stomach, bronchi, ovaries, prostate, colon (colorectal cancer)) and autoimmune processes in the body (autoimmune thyroiditis, rheumatoid arthritis, Sjögren’s disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, etc.). The pathogenetic substrate of the syndrome is autoimmune mechanisms.
Generation and sex distribution Lambert-Eaton disease is close to myasthenia (M), said to the genetic association with HLA-B8-DR3. Increased risk of autoimmune diseases was detected in patients with Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome and their family members. The first description of Lambert-Eaton syndrome dates from 1953. The condition was discussed in detail in 1957 by the American neurophysiologist Lambert and neurologist Eaton. It was later named after them.
What is Lambert-Eaton Syndrome?
The disease is a myasthenic syndrome associated with autoimmune and malignant tumor processes. It is characterized by variable muscle weakness and autonomic nervous system dysfunction, meaning that the muscles cannot contract properly, leading to muscle weakness and other symptoms often associated with small cell lung cancer (SCLC).
Its approximate frequency is 0,48 cases per 1 million population. However, for example, in the Netherlands, this figure is 0,78 cases and correlates with the prevalence of 3,42 cases per 1 million in the total population. It affects people between the ages of 20 and 70. Most often, their age exceeds 40 years. Initially, the syndrome was detected in males.
According to various experts, the disease occurs as a paraneoplastic syndrome in most affected people (50 to 75% of the total).
- Most of them are men (about 70%).
- In women, it is rare (up to 20%).
- Most of the tumors (80%) detected in Lambert-Eaton syndrome are caused by small cell lung cancer.
In this case, myasthenic syndrome can occur several years before the tumor is formed. Occasionally, Lambert-Eaton syndrome is accompanied by other paraneoplastic syndromes, particularly paraneoplastic polyneuropathy.
What are the Main Causes of Lambert-Eaton Syndrome?
The main factors in developing LEMS may be malignant neoplasia or an autoimmune process. In autoimmune diseases, the immune system mistakes your body for a foreign object. Your immune system produces antibodies that attack your body.
- Your body attacks the nerve endings that control the amount of acetylcholine. Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter that causes muscle contractions. Muscle contractions allow you to make voluntary movements such as: walking, wiggling your fingers, and shrugging.
- Specifically, your body attacks the voltage-gated calcium channel protein (VGCC). VGCC is required for the release of acetylcholine. You do not produce enough acetylcholine with VGCC injection, so your muscles cannot work properly.
- Many cases of Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS) are linked to lung cancer. Researchers believe that cancer cells produce the protein VGCC. This causes your immune system to produce antibodies against VGCC. These antibodies then attack both cancer cells and muscle cells. Anyone can develop LEMS in life, but lung cancer may increase the risk of developing this disease. You may be at higher risk if your family has a history of autoimmunity.
What are the Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome Symptoms?
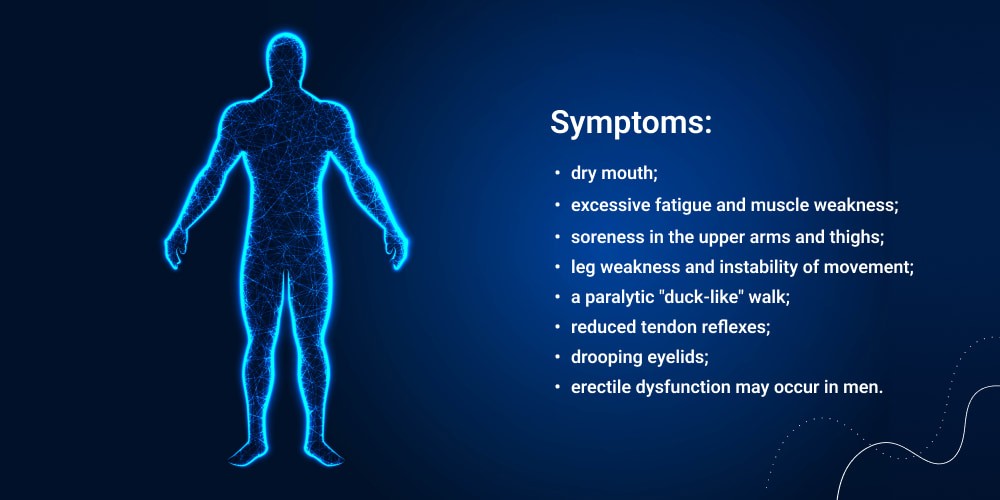
Symptoms may include:
- dry mouth;
- excessive fatigue and muscle weakness;
- soreness in the upper arms and thighs;
- leg weakness and instability of movement;
- a paralytic “duck-like” walk;
- reduced tendon reflexes;
- drooping eyelids;
- erectile dysfunction may occur in men.
When examining patients with Lambert-Eaton disease, the majority (90%) have antibodies to calcium channels, which consist in the structure of motor nerve fiber endings and tumor cells. The autoimmune attack targets the presynaptic membrane of the neuromuscular synapse. Its disruption results in a decrease in the release of the neuromuscular transmission mediator acetylcholine, which disrupts the passage of excitation from the nerve fiber to the muscle. This process manifests in the body the main symptoms of the syndrome: excessive fatigue and muscle weakness.
As the myasthenic disease progresses, you will also experience:
- When the patient is interviewed, they complain of leg weakness and instability of movement, which is more pronounced when walking and climbing stairs for long periods of time;
- Patients with Lambert-Eaton disease tend to have a paralytic “duck-like” walk;
- Tendon reflexes are reduced;
- Lambert-Eaton syndrome has a definite increase in muscle strength during movement, which distinguishes it from myasthenia gravis, where muscle weakness increases with movement.
Accompanying symptoms may also include:
- discomfort in the back and neck;
- paresthesias in the distal limbs;
- myalgia;
- decreased vision acuity;
- various autonomic disorders, such as decreased lacrimation, dry mouth, orthostatic arterial hypotension, and distal hyperhidrosis.
In some cases, upper eyelid drooping is found. Rarely impaired swallowing, double vision, and myasthenia gravis movement disorders have been noticed.
How to Treat Lambert-Eaton Syndrome?
Anticholinesterase drugs, corticosteroids and cytostatics are used to treat the disease. Therapeutic plasmapheresis is carried out. Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome is a rather complex disorder with many inherent symptoms. For this reason, it is treated as an inpatient condition. The treatment of Lambert-Eaton syndrome depends on what caused it:
- If the origin of Lambert-Eaton syndrome is due to the manifestation of a malignant tumor, therapy is primarily aimed at eliminating it. When the cancer is treated positively, the symptoms of Lambert-Eaton syndrome are also reduced.
- If the origin of the disease is autoimmune, symptomatic treatment is carried out. For this purpose, drugs (most often glucocorticosteroids) that suppress the immune system are used. Plasmapheresis procedures filter the autoantibodies circulating in the blood.
- Experts suggest taking a medication called acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, which promote this through the accumulation of acetylcholine in the synapse. It is needed to restore nerve impulse conduction along the neuromuscular synapse. These include pyridostigmine and ipidacrine.
- Lambert-Eaton syndrome therapy often uses healthy human immunoglobulin, administered intravenously to the patient. Potassium preparations are prescribed to improve muscle contraction, which also positively influences the passage of the nerve impulse. Cytostatics and hormones are used in the treatment process to reduce the severity of the destructive processes in the human body.
Schedule a Consultation with Lone Star Neurology
At Lone Star Neurology, we have highly qualified doctors with years of experience helping patients facing neurological issues, particularly with LEMS diagnosis. We have a highly experienced neurologist staff who are both professional and compassionate, and empathetic at the same time. So, the patient’s state of health can be made close to normal by removing antibodies from the blood after treatment.
Our doctors recommend that patients exercise and take walks outdoors. It is essential to follow the treatment regimen prescribed by the doctor, take the medication on time, and observe the doses recommended by the neurologist.
FAQ
- What is the difference between myasthenia gravis and Lambert-Eaton syndrome?
Eaton-Lambert syndrome is caused by antibodies that interfere with the release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. While myasthenia gravis leads to muscle weakness and myasthenic crises. This distinguishes Eaton-Lambert syndrome from myasthenia gravis.
- How long can you live with Lambert-Eaton syndrome?
It is vital for myasthenia gravis patients to monitor their health and to treat comorbid conditions in good time and prevent their progression. If all conditions are fulfilled, living to a fairly advanced age is possible.
- How is Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome diagnosed?
The LEMS diagnosis is made by a neurologist based on the examination of the patient, a neurological examination and the results of an electroneuromyography.
- Is Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome progressive?
The Lambert Eaton disease can be progressive without proper treatment and care. To maintain a normal body, a person with myasthenia gravis should maintain a healthy lifestyle, a proper diet, regular physical exercise, adequate rest, and try to avoid stress.











Please, leave your review
Write a comment: