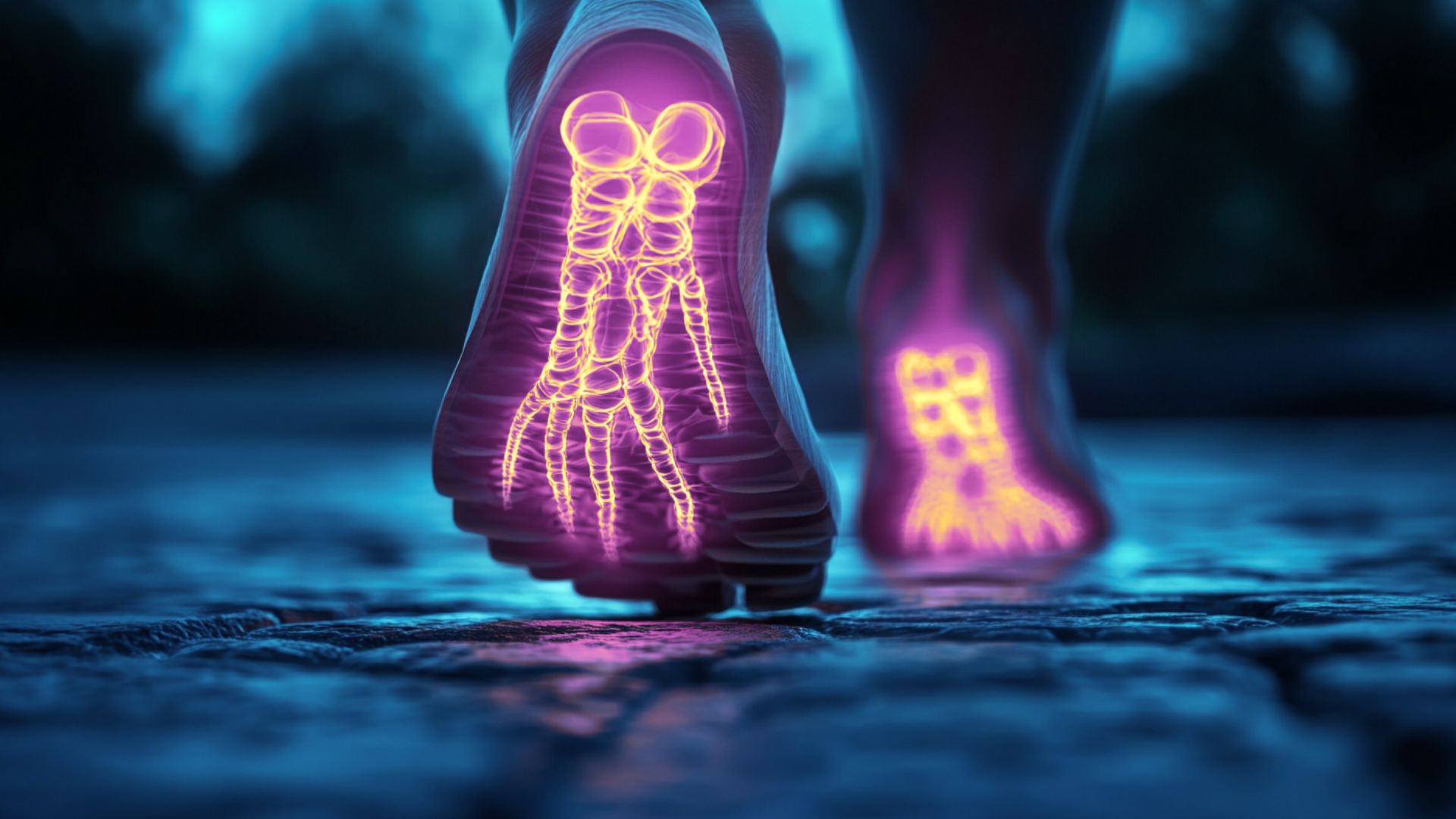
Neuropathy is a condition that affects the peripheral nerves, which connect the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body. When these nerves become damaged, they can no longer transmit signals for movement, sensation, and bodily functions properly. This damage often causes numbness, tingling, burning pain, or weakness, particularly in the hands and feet, which can significantly disrupt daily life.
Simple tasks like walking, holding objects, or buttoning a shirt may become challenging when you have neuropathy. The pain or loss of sensation can increase your risk of falls or injuries, and some people experience muscle cramps or difficulty sleeping due to ongoing discomfort.
Peripheral neuropathy can stem from various causes, including diabetes, infections, injuries, and vitamin deficiencies. The impact varies widely, ranging from mild discomfort to severe disability that affects mobility, work performance, and emotional well-being. Managing symptoms through medication, therapy, and lifestyle modifications is crucial for maintaining a high quality of life.
Common Causes of Neuropathy
Neuropathy results from damage to the peripheral nerves, causing symptoms such as numbness, tingling, or pain. Understanding the most common neuropathy causes is essential for prevention and treatment.
Diabetes is the leading cause of neuropathy in the United States. High blood sugar levels damage nerves over time, with diabetic neuropathy affecting approximately 50% of people with diabetes. This often causes numbness or pain in the extremities, particularly when blood glucose levels are not well controlled. The longer someone has diabetes and the less controlled their blood sugar, the greater their risk of developing nerve damage.
Physical injury represents another major cause. Trauma from accidents, repetitive stress, falls, fractures, or surgeries can compress or sever nerves, directly damaging nerve fibers. Car accidents, sports injuries, and workplace incidents commonly lead to this type of nerve damage. Even seemingly minor repetitive motions, like typing or using vibrating tools, can gradually damage nerves over time.
Vitamin deficiencies, especially a lack of B vitamins, significantly impair nerve health. Vitamin B12 deficiency is particularly problematic, as this vitamin is essential for maintaining the protective covering around nerves. These deficiencies can result from:
- Poor dietary choices lack essential nutrients
- Absorption issues related to digestive disorders
- Certain medications that interfere with vitamin uptake
- Age-related changes in nutrient absorption
While these are the most common causes, neuropathy can also result from infections, autoimmune diseases, or exposure to toxins. Certain infections like shingles, HIV, or Lyme disease can damage nerves. Autoimmune conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis may cause the immune system to attack nerve tissue.
Recognizing Neuropathy Symptoms
Neuropathy symptoms develop when peripheral nerves become damaged, disrupting the signals responsible for sensation and movement. The intensity varies from person to person and may appear gradually or suddenly. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for obtaining a proper diagnosis and neuropathy treatments.
Tingling is often the first symptom people notice. This prickling sensation, often referred to as “pins and needles,” typically occurs in the hands or feet, sometimes feeling like electric shocks. This tingling can be constant or intermittent and frequently worsens at night, disrupting sleep. Many people describe it as a buzzing or crawling sensation under the skin.
Numbness represents a more serious symptom. This loss of sensation causes affected areas to feel “asleep” or completely numb to the touch. You might not feel temperature changes, which means you could burn yourself without realizing it, or you might not notice cuts or injuries. This creates a dangerous situation because unnoticed wounds can become infected. Numbness typically affects the extremities first, starting in the toes or fingers and spreading gradually if left untreated.
Muscle weakness significantly impacts daily functioning. Your muscles feel weak or heavy, reducing your overall strength and making simple tasks challenging:
- Gripping objects becomes difficult
- Walking feels unsteady and requires more effort
- Climbing stairs becomes exhausting
- Frequent stumbling or dropping things occurs
- Balance problems increase fall risk
Beyond these primary neuropathy symptoms, many people experience burning pain that feels like their feet or hands are on fire. This pain can be severe and constant, making it difficult to wear shoes or tolerate bed sheets touching the affected areas. Muscle cramps and spasms are also common, often occurring at night.
The severity of symptoms depends on the extent of nerve damage and its underlying cause. Symptoms can disrupt sleep, work performance, and emotional well-being, often leading to depression or anxiety.
Understanding Nerve Damage Progression
When conditions causing nerve damage go untreated, nerve function deteriorates over time. If nerve damage continues to progress, it can seriously impair daily activities and overall quality of life.
Worsening neuropathy symptoms represent the first stage of progression. What begins as mild tingling or occasional pain can escalate to constant burning sensations or severe discomfort that disrupts sleep and daily activities. The affected area may expand, spreading from just the toes to the entire foot, or from fingertips to the whole hand.
Loss of function marks the next stage. Ongoing damage progressively reduces nerve signaling capacity, causing increasing muscle weakness, coordination problems, or complete loss of sensation. Your balance may deteriorate, making walking dangerous. Fine motor skills decline, making tasks such as buttoning shirts, writing, or picking up small objects nearly impossible to perform.
Serious complications develop in advanced cases. Persistent nerve damage can lead to infections or ulcers, particularly in areas where sensation is lost. When you can’t feel pain, you might not notice injuries that can become infected. In severe cases, this may result in permanent disability or even require amputations.
Nerve damage progression is most commonly seen in diabetes, where chronically high blood sugar continuously harms nerves. However, untreated infections, injuries, or vitamin deficiencies can also accelerate damage if ignored.
Diagnosis and Testing
Diagnosing peripheral neuropathy involves comprehensive examinations and specialized tests. An accurate diagnosis is crucial for guiding effective treatment and preventing further disease progression.
The diagnostic process typically includes:
- Physical examination: Assessment of reflexes, muscle strength, and sensation throughout the body
- Nerve conduction studies: Measurement of how quickly nerves transmit electrical signals
- Electromyography (EMG): Evaluation of electrical activity in muscles to detect abnormal patterns
- Blood work: Screening for diabetes, vitamin deficiencies, thyroid problems, and infections
- Imaging studies: MRI or CT scans to rule out structural problems like herniated discs or tumors
- Skin biopsy: Assessment of small nerve fiber damage in early-stage cases
These tests work together to identify the location, severity, and underlying cause of nerve damage, allowing doctors to create an effective treatment plan.
Treatment and Management
Neuropathy treatment focuses on relieving symptoms and addressing underlying causes. Effective treatment can significantly improve daily functioning and overall quality of life.
Medications play a central role in managing neuropathy symptoms:
- Gabapentin or pregabalin: Specifically target nerve pain as first-line treatment
- Duloxetine: Effective for managing chronic nerve-related discomfort
- Capsaicin cream: Provides localized relief without oral medication side effects
- Pain relievers: Over-the-counter or prescription options for additional relief
Lifestyle changes are equally important for managing neuropathy:
- Regular exercise (walking, swimming, cycling) improves circulation and nerve health
- Balanced diet rich in B vitamins corrects nutritional deficiencies
- Strict blood sugar control prevents further damage in diabetic neuropathy
- Avoiding alcohol and tobacco supports nerve repair
- Maintaining a healthy weight reduces nerve strain
Therapeutic approaches complement medical neuropathy treatment:
- Physical therapy: Strengthens muscles, improves balance and coordination
- Occupational therapy: Teaches adaptation of daily tasks and the use of assistive devices
- TENS therapy: Uses mild electrical impulses to reduce pain signals
- Complementary treatments: Acupuncture, massage, or meditation for additional relief
Living Better With Neuropathy
Managing peripheral neuropathy requires daily attention to prevent complications and maintain quality of life. Key strategies include:
Pain management techniques:
- Taking prescribed medications as directed
- Applying topical neuropathy treatments for localized relief
- Using warm baths or a gentle massage to soothe discomfort
- Practicing relaxation techniques to manage stress-related pain
Preventive measures:
- Inspecting feet daily for cuts, sores, or injuries
- Wearing comfortable, well-fitting shoes with proper support
- Controlling blood sugar levels if diabetic
- Avoiding repetitive motions that could cause injury
Daily health habits:
- Eating nutritious meals with adequate vitamins
- Exercising regularly to boost circulation
- Getting adequate sleep to support nerve health
- Staying hydrated throughout the day
By combining medications, lifestyle modifications, and various therapies, most people with neuropathy can manage their symptoms effectively. The key is working closely with your healthcare team, adhering to a consistent treatment regimen, and making adjustments as needed. Regular check-ups enable ongoing monitoring of symptoms and allow for optimized treatment. Support groups can provide valuable emotional support and practical advice from others who understand the challenges of living with neuropathy.












I've given up... the stress her office staff has put me through is just not worth it. You can do so much better, please clean house, either change out your office staff, or find a way for them to be more efficient please. You have to do something. This is not how you want to run your practice. It leaves a very bad impression on your business.
Please, leave your review
Write a comment: