One of the neurologic disorders occupying the carotid artery is carotidynia. These painful pulse sensations in the neck qualify as terribly annoying discomfort which does not provoke fatal consequences for patients. Otherwise, long-term painful reactions make the patient’s life changeable and lead to severe problems over time.
Although the disorder’s nature is pretty understandable, many neurological researchers have still discussed its triggers and forms of appearance. The primary symptoms of this neurological ailment are the dimensions of carotid artery enlargement and pressure-like pain affecting the appropriate neck zone. Other carotidynia signs are facial pain due to deteriorated blood circulation and migraine. They can exhaust health and mental strengths obtrusively.
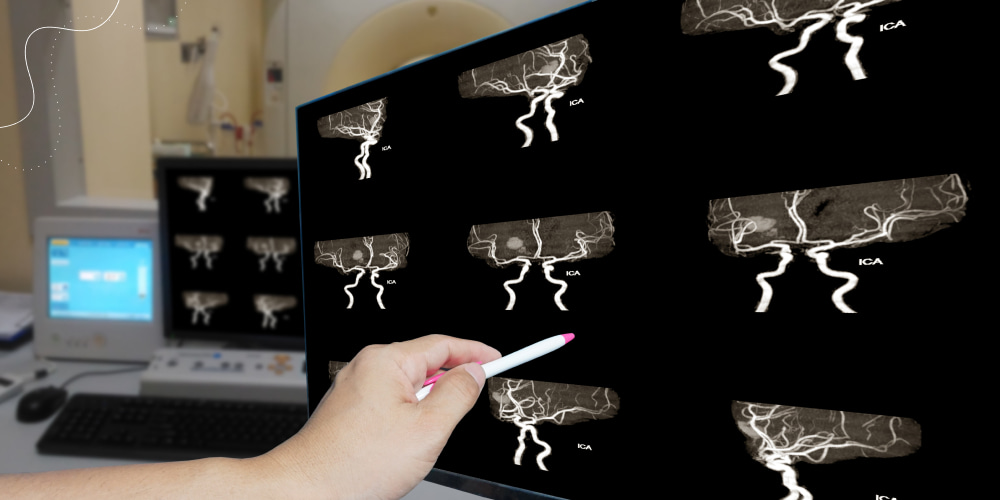
Every potential patient should be consulted with an experienced specialist and receive all necessary examination procedures, including MRI or CT, to prevent the effects of this disorder. The in-time diagnosis will grant effective treatment to reduce negative consequences which spoil everyday activities.
What is Carotidynia?
Carotidynia refers to neurological disorders in the one-sided facial and neck area. Its significant feature is pain focused primarily on the left side of the face or neck artery. This ailment qualifies as a migraine subtype and drastically spoils normal living conditions.
The overall pain could be immediate and severe, complicating the patient’s life. The disease is rare and requires permanent examination to ensure the diagnosis’s reliability. The pain nature defines this disease as an idiopathic syndrome because it could be identified at any time, and the real triggers are still unclear.
The pain intensity grows gradually; however, its nature becomes pulsive. Anyway, such painful perceptions jeopardize the normal functions of the other cells and tissues and affect human behavior. Patients who suspect painful neurological abnormalities need to detect core symptoms interrupting their everyday activities and ask for medical aid for a comprehensive examination.
Carotidynia Symptoms
Carotidynia symptoms are characteristic of typical pain reactions accompanied by carotid artery pathologies. They include:
- Pulse pain periodicity located in the neck zone, especially the left side;
- Facial migraine;
- Jaw pain;
- Toothaches;
- Earaches;
- Slightly visible inflation when the carotid artery is deteriorated;
- Severe migraine, which could provoke the carotidynia syndrome or supplement the painful reactions due to abnormal blood circulation to the central nerve center.
This neurological disorder has a short list of the identified evidence because of the ongoing scientific discussions about its nature and triggers provoking complicated disturbances.
Classification of Symptoms
Painful perceptions concentrated in the left-side facial or neck area will highlight several neurological disorders with similar symptoms. Nevertheless, the cutting-edge clinical test and procedures help classify the carotidynia subtypes due to their pathological nature:
- Symptomatic pain. This unpleasant sensation depends on the physical abilities of the trifacial nerve. This nerve visually divides the side face into three parts according to anatomical features. Any external or internal factor could provoke painful reactions in the eye, cheek, or neck area, resulting in carotidynia. These pathological pains could occur and spoil the normal living conditions. The symptomatic carotidynia qualifies as a mild stage of the disease development and could be eliminated through the well-prescribed recovery program.
- Neurogenic pain. This subtype allows split theories about the genetic origin of the sudden or permanent painful reactions affecting facial or neck carotid arteries. As this neurological disorder is indicated among a few persons per 100 000 people worldwide, some specialists point out gene modifications that lead to low strengths of artery walls. Otherwise, any inherited neurological pathology could become the direct reason for carotidynia development.
- Psychogenetic pain. The facial or neck painful pathology could be grounded on psychological factors. Depression, impulsive obsession or other related disorders complicate the treatment process and lead to intensive pulsing aches. The psychosomatics aspects are the severest reasons to develop this pathological disease.
Carotidynia Causes
All neurological experts have tried to find carotidynia causes and its painful reactions in the neck provoked by abnormal carotid artery modifications.
- The vast majority of the medical society agrees that the core trigger which induces pain reactions is inflammatory processes inside the carotid artery.
- Clinical tests like biopsy show inflammation in the lymphocyte cells, which deteriorate extremely pulse pain in the neck, face, or jaw.
- The chronic inflammatory processes modify the carotid artery structures and make its walls inflexible or indurated. However, these modifications do not affect the anatomical structure of the head, neck, or jaw. Therefore, carotidynia differs from the analogous neurological disorders which restrict normal living conditions.
- Some experts highlight the psychological impact on carotid deterioration development.
- Emotional or mental disbalances and constant stressful situations also initiate the inflammatory changes in the neck arteries.
Carotidynia Diagnosis
The Carotidynia diagnosis consists of:
- Physical examination
- MRI, CT, or X-ray diagnosis
- Specific blood test
The neurologist’s most effective approach is to examine the patient thoroughly and exclude all possible disorders and ailments related to pulse pain in the neck area. The recommended tests like blood tests show the general health history and focus on detecting fatal diseases or pathological states.
Let’s look at the methods of diagnosis in more detail:
- Physical examination of the painful area and efforts to find the epicenter of the pulsing artery. Most patients consider this procedure more complicated than other applicable clinical tests. Its purpose is to localize the pathological pain trigger and compare both neck sides to find the visually bigger one. However, the neurological conclusion requires a detailed medical assessment;
- MRI, CT, or X-ray diagnosis of the head and neck. The received images visualize the neck tissues and detect the absence or existence of the inflammatory factors. The previous medical testing results prove that people with carotidynia syndrome have an inflamed carotid artery, which the experienced neurologists could notice on the neck scanning images;
- Specific blood tests to detect inflammation sources and exclude the versions about bacteriological or infection triggers. For carotidynia-positive people, such tests are normal and have no abnormality.
How to Treat Carotidynia?
The carotidynia treatment program is drafted by the treating neurologist authorized to amend it or cancel some recommendations.
The general concept for curing people with disordered carotid arteries involves several blocks:
- Medicine products
- Physical exercises
- Nutritional diets
Let’s take a closer look at the types of treatment:
- Medicine products. The pharmaceutical prescriptions are sophisticated and contain chemical substances capable of reducing painful perceptions. As many neuralgia states, carotidynia symptoms are removed by steroids. As such, neurologists regulate the acceptable dosages and decline them once the patients perceive significant health improvements. However, applying steroids in a peroral or injection method requires the proper medical monitoring and control to avoid addictive habits among the targeted patients.
- Physical exercises. The patients suffering from pulsing pain in the neck zone can conduct easy physical exercises to maintain the treatment achievements. Slight yoga or pilates movements foreseen in anti-migraine programs benefit the comprehensive therapy strategy to strengthen the overall neurological state of the patients with carotidynia syndromes. Aroma therapy also provides treatment and relaxing effects. However, massage sessions could be prohibited due to the high risks of the ailment progress. Any physical activity should be adjusted with the treating neurologist and the patient’s clinical diagnosis results.
- Nutritional diets. To prevent carotidynia signs after the patient’s recovery, the neurologists suggest balancing nutrition stimulating cardiovascular functions and nerve rehabilitation. Foods enriched in vitamin K, B, and E strengthen the immune system and improve blood circulation.
History and Etiology of Carotidynia
The term carotidynia refers to the intense painful reactions in the left side of the neck where the carotid artery is detected. The inflammatory processes inside the artery provoke unpleasant, annoying ache effects. Therefore, the name of the artery is identified as one of the most discussed neurological disorders in the medical community.
The first mention of the carotidynia syndrome is dated 1927 and belongs to Fay – a neurologist who diagnosed a tenderness of the carotid artery characteristic of throbbing pain. However, the neurology of the XX century classified neck-located pain as a migraine symptom or associated it with other disorders.
In 1994, Biousse and Bousser offered a separate term that specified the particularities of the inflamed carotid artery. The cutting-edge neurological studies and techniques describe symptoms and treatment plans for this ailment. Nevertheless, some scientific gaps about the carotidynia triggers could help prevent the disease.
Lone Star Neurology Deals with Numerous Painful Reactions in Your Neck
Carotidynia could not be treated with a neglected attitude and tons of pain-reducing capsules. Indeed, this neurological abnormality could become a consequence or trigger of a more severe disorder, complicating the overall recovery strategy. Our professional neurologists offer you a range of services and clinical assessment mechanisms to discover the genuine nature of your neck pain in different cities of Texas, including Dallas, Fort Worth, and others.
FAQs
- What causes carotidynia?
The neurological sciences could not name the factors that provoke the carotid artery’s pulsing pain. The main reason is inflammatory processes in the neck artery localized on the left side. However, identifying the ties between inflammation and severe painful effects is unclear and requires the proper medical diagnosis.
- How do you treat carotidynia?
The neurologists prescribe pain elimination pharmaceutical products or steroids. The dosage depends on the pain’s nature and its intensity. The patients are not allowed to correct the treatment plan alone and without medical control. However, physical activities and dietary nutritional formulas full of vitamins and minerals are welcome for the recovery process.
- How long does it take for carotidynia to go away?
Each treatment effect depends on the diagnosed consequences of the existing ailment. Usually, carotidynia symptoms disappear in a week if the patients follow the neurologist’s recommendations. However, the severe pain cases could last for a few weeks and are always finalized successfully.
- Does carotidynia cause ear pain?
The intense pain covering the neck could spread to the ear or forehead zones. Also, you might face migraine caused by deteriorated carotid artery syndrome.
- Which side of the neck is the carotid artery?
The left side of the neck is diagnosed as the carotidynia-affected zone. The reason is that the carotid artery inflamed by pathological triggers goes on the neck’s left side.













Please, leave your review
4 Comments
Meryl
19/07/2023
Informative and helpful information in this clear and detailed article.
Mahmoud
02/10/2023
That was very informative but I’d like to know if it comes back after it goes. Once it’s over does it come back again after a few months and if so then how long do these relapses last for?
KARIMA
05/04/2024
On my experience yes it will come back, actually i have this desiese im so sad
Lindsey heath
01/02/2024
I have had several bouts of carotidynia. (My neurologist calls it TIPIC syndrome).It has been visualized on multiple PetCt and CTA scans.
I would love to know more about what triggers it as I am nervous that having recurring inflammation is doing permanent damage to the artery.
Write a comment: