Spinal stenosis is a chronic pathological process characterized by a decrease (narrowing) in the size of the spinal canal and intervertebral foramen due to the growth of bones and cartilage. According to the norms, the sagittal (anteroposterior) size of the spinal canal at the lumbar level is 15-25 mm, the transverse size is 26-30 mm. Further, these indicators are the “cauda equina” (bundle group of roots). Relative stenosis – reduction of the anteroposterior dimension to 12 mm. In this case, clinical manifestations may be completely absent. A decrease to 10 mm or less is called absolute stenosis of the spinal canal. It already has clinical signs.
The spinal canal protects the spinal cord, which is inside the vertebrae. The spinal cord and brain are the CNS (central nervous system) that regulates the functions of the human body. For the normal functioning of the spinal cord, the spinal canal mustn’t be damaged.
Spinal stenosis forms:
- in front – the body of the vertebrae;
- intervertebral discs;
- behind and on both sides – the arches of the vertebrae (they are connected by a special biological yellow ligament).
Looking at it in cross-section, you can see that it can be either round or oval.
The spinal canal includes:
- the spinal cord with paired nerve roots, which depart from it and go beyond this channel through their specific openings (they are surrounded by the dura mater);
- loose and adipose connective tissue, which consists of nerves, arteries, and veins;
The spinal canal performs two main functions:
- Conductor (sends and transmits a nerve impulse from the center of its location to the periphery, and then returns this signal)
- Reflex (forms a response to all kinds of irritations from the nervous system).
Spinal stenosis is a fairly common, slowly progressive disease. With age, every person develops aging processes of the spine, which are manifested by degenerative processes. In a lonestarneurology, you can find detailed information about this disease.
Classification and Symptoms of Spinal Stenosis
Classification
- Central stenosis, when the lumen of the canal narrows towards the arch (from the body), the anteroposterior size decreases;
- Lateral stenosis, in which the narrowing reaches 4 mm;
- Combined stenosis with a combination of symptoms.
Spinal stenosis is relative when the diameter of the spinal canal is 10-12 mm. Treatment is conservative and has a good prognosis. In the absence of timely treatment, negative changes will increase.
Symptoms
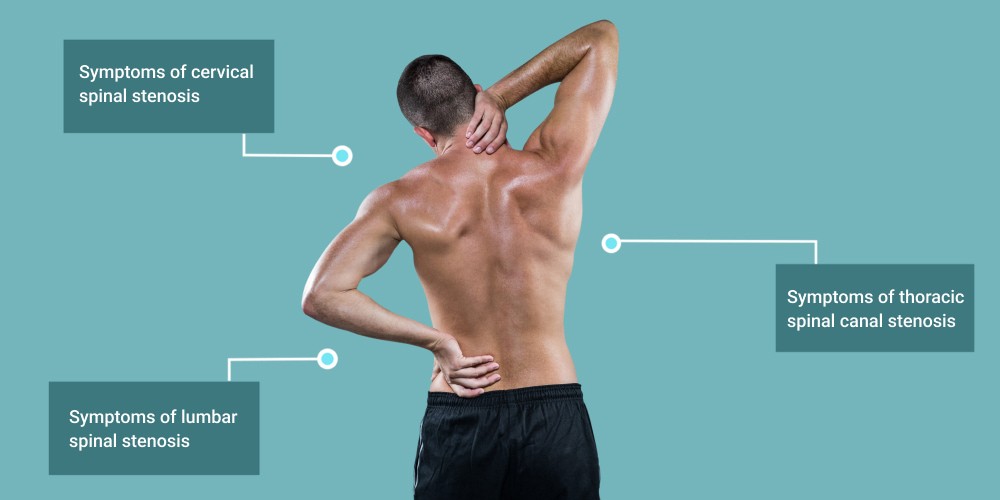
Symptoms of lumbar spinal stenosis:
- pains of an acute, chronic nature, starting in the lumbar region, passing along the leg to the foot;
- lameness;
- early fatigue when walking;
- decreased reflexes of the lower extremities;
- paralysis (paresis) of the lower limbs or decreased muscle strength;
- muscle atrophy of the lower extremities;
- violation of sensitivity in the groin, genitals, and legs (burning, numbness, tingling);
- dysfunction of the bladder and anal sphincter;
- thinning (weight loss) of the legs due to dystrophic pathologies;
- erectile dysfunction in men.
Symptoms of cervical spinal stenosis:
- pain in the occipital region, neck, and shoulder region;
- a decrease in the strength of the muscles affected by the disease;
- elements of sensitivity (numbness, tingling in the neck and shoulders);
- violation of respiratory function and possible respiratory arrest;
- below the level of the lesion, the development of paralysis, and (or) complete loss of sensitivity.
Symptoms of thoracic spinal canal stenosis:
- pain in the chest area at the site of the lesion;
- pain syndromes in the region of the heart;
- the pain of the internal organs of the abdominal cavity;
- the sensitivity of the skin in the abdomen and chest area may be impaired;
- dysfunction of the pelvic organs.
Causes of Spinal Stenosis
Before starting the treatment of lumbar or cervical spine stenosis, you should find out what causes the onset and development of the disease.
A congenital or primary type of stenosis is formed during the intrauterine development of the human embryo. It happens in the period from 3 to 6 weeks of development. The genetic factor plays a role here. But absolute stenosis of the spinal canal can develop due to infectious and toxic factors affecting the fetus.
Also, the cause of congenital stenosis is:
- Chondrodystrophy or achondroplasia (chronic), manifested in intrauterine bone growth disorders. In this case, the spinal canal narrows due to the shortening or thickening of the arches of the vertebrae and the fusion of the vertebrae.
- Diastematomyelia. It is characterized by a bifurcation of the spinal cord, separation of the spinal canal by a septum (it consists of either bone or cartilaginous tissue).
Secondary spinal stenosis appears and develops in childhood or already in adulthood. This development may be due to the following reasons:
- traumatic displacement of the vertebrae or intracanal hematomas;
- changes in the intervertebral joints, which are manifested in the proliferation of bone tissues inside the spinal canal;
- anatomical defect of the arch of the spine;
- intervertebral hernia;
- inflammation in ankylosing spondylitis (in this case, the capsules of the intervertebral joints thicken);
- Forestier disease;
- cysts and tumors that appear inside the spinal canal.
Regardless of the cause, treatment of spinal stenosis should begin when the disease is detected.
Risks and Complications of Spinal Stenosis
Risk factors
There is a category of people who are most susceptible to the disease of absolute stenosis of the spinal canal at the level of the lumbar, chest, and neck.
- Mainly, elderly people suffer from this disease due to age-related changes and degenerative vertebral diseases. In the age group (50 years and older), this figure is 1.8-8%.
- Acquired stenosis of the spinal canal occurs most often at the level l5 s1 and l4 l5 of the last stage of osteochondrosis of the spine when the bone tissue of the vertebral bodies and osteophytes is actively growing.
Complications
If you do not start the treatment of the lumbar, cervical, or thoracic spine stenosis timely, pathological manifestations of this disease are possible. Complications can occur if there are other spinal injuries (sports injury, fall from a height, etc.). In this case, there is an increase in the compression of the spinal cord. Hematomas, scars, fragments of the spine, and displaced vertebrae can put pressure on it.
The most serious complications are:
- Paralysis of the legs, stable paresis.
- Sexual dysfunctions.
- Dysfunction of the pelvic organs.
- Loss of sensitivity in the lower torso.
The rarest inflammatory processes occur in the nerve elements, membranes, and vertebrae because, after the operation of the stenosis of the spinal canal of the lumbar spine, strong antibiotics are used. It is not uncommon that the consequences after surgery for lumbar, cervical, and thoracic spine stenosis give more severe consequences than the disease itself.
Diagnosis of Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis is a pathology that the doctor may suspect even during the initial conversation with the patient. The neurosurgeon pays attention to the characteristic pain in the lumbar spine of the back, discomfort in the legs, and other symptoms described above. Initial contact with medical personnel is more often at the level of a general practitioner or family doctor. These specialists, having identified typical symptoms, refer the patient to a neurosurgeon.
In addition to collecting anamnesis and analyzing patient complaints, the following methods are used to diagnose the disease:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the spine. This method is a mandatory procedure that allows you to fully visualize the spinal canal and establish areas of compression of nerve fibers.
- Survey spondylography with functional tests in the anterior and lateral projection. This procedure is used for a comprehensive assessment of the state of the spinal column and its bone structures in dynamics.
The above methods are mandatory for establishing the localization of the pathological process and assessing the severity of the patient’s condition. For more accurate information, the neurosurgeon may also prescribe:
- spine ultrasound;
- spiral computed tomography (SCT);
- blockade of intervertebral joints;
- selective blockade of the roots of the spinal cord.
Also, the doctor prescribes a standard set of laboratory examination methods, which includes a general blood and urine test and a biochemical blood test.
Treatment of Spinal Stenosis
Conservative treatment
In the absence of pronounced neurological changes, when the pain is only in the legs and lower back and seeking medical help is timely, it is possible to use conservative methods to treat spinal stenosis. These methods include:
- anti-inflammatory drugs to eliminate pain and inflammation, reduce tissue swelling;
- muscle relaxants to reduce muscle tension in the lumbar region;
- medication blockade with intervertebral administration – hormonal drugs relieve pain at the site of its occurrence quickly and effectively;
- vascular agents that improve blood flow in the affected vessels;
- back massage sessions;
- a diverse range of physiotherapy – exposure to currents, electrophoresis, magnetotherapy, mud treatment;
- exercise therapy is a set of therapeutic exercises to improve health and reduce pain.
The complex use of all these techniques gives a positive result. The selection of a therapy program should be carried out separately in each case, taking into account the existing contraindications.
Surgery
The purpose of the operation is to exclude compression of the roots of the spinal nerves. Large open and endoscopic surgeries are performed when tissue incisions are minimal.
The following techniques are most commonly used:
- Decompression cervical laminectomy – expansion of the spinal canal by removing individual elements – the spinous process, part of the ligamentum flavum, and the vertebral arch. The method is traumatic.
- Stabilizing surgery to enhance the supporting function of the spine – the application of metal braces after the expansion of the spinal canal.
- Microsurgical decompression and using fixation systems to strengthen the spinal column after elimination of stenosis; the function of flexion and extension of the spine is preserved.
- If the source of spinal stenosis is a herniated disc, then a microdiscectomy is performed, possibly in combination with a cervical laminectomy.
Usually, the use of surgical methods ensures the patient’s recovery. For the best results, it is important to behave correctly in the postoperative period, follow the recommendations of doctors and carry out rehabilitation measures.
Prevention of Spinal Stenosis
Recommendations for the prevention of spinal stenosis are reduced to the well-known elementary advice for maintaining a healthy back.
1. Good posture since childhood
Poor posture affects early impairment of the musculoskeletal system. Modern children grow up fast. Muscle mass does not keep pace with the growth of the skeleton; therefore, the muscle frame in children is underdeveloped and bone structures are vulnerable. Children need to be given increased attention from an early age. From childhood, children must be taught to keep their backs straight. In the future, parents must correctly organize the child’s workplace:
- you need to sit on a chair with a back;
- legs need supporting;
- the seat should be neither too hard nor too soft;
- furniture should be matched to height.
It is necessary to organize the perfect resting place to prevent spinal stenosis:
- sleeping on an orthopedic pillow and mattress;
- while watching TV, you should not lie down, due to overstrain of certain muscles, blood flow in the cervical and lumbar spine is disturbed;
- the center of the screen should be projected to the middle of the bridge of the nose.
There are many effective posture exercises – walking in a straight line with a book on your head, walking with a stick behind your back, and balance exercises. Choreography, dancing, equestrian sports, gymnastics help the optimal position of the spine. Also, backpacks shouldn’t be heavy.
2. Knowledge of the laws of ergonomics
Everyone should know the rules of controlling their body.
- Any weight should be lifted not with a jerk but carefully with an even back, gently straightening the extended lower limbs.
- The muscles of the legs should work, not the spine.
- If you have to carry a load of more than 5 kg, it must be distributed evenly between both hands. It is better to replace the bag with a backpack.
3. Sleep well on the right surface in the correct posture
- You need to sleep on a high-quality mattress that prevents the body from sagging. Too hard a mattress forcibly straightens the natural curves of the spine.
- The pillow should be equal to the shoulder height.
- The fetal position (lying on its side with the knees pulled up to the abdomen) is the optimal sleeping position for the spine.
- Doctors do not recommend sleeping on the stomach.
4. Regular physical activity
Professional sports are harmful to health – this is the opinion of experts. Extreme stress quickly leads to the deterioration of the human body and spinal stenosis. Muscle mass is growing so actively that the heart does not have time to provide it with nutrition. But health-improving gymnastics, classes in fitness clubs and sports complexes bring undoubted benefits if the choice of exercise is approached thoughtfully.
- Daily exercise protects the spine from premature wear and tear. It is advisable to perform elementary exercises regularly for 30 minutes a day.
- You should visit the pool, do water aerobics, yoga, and include stretching exercises in your workout.
- Light dumbbell exercises and oriental health-improving gymnastics are also useful. Before training, you must remember about the mandatory warming up of the muscles. A strong and well-formed muscle corset supports the spine and the entire body. In addition, physical activity helps to stay slim, which means it protects the spine from being overweight.
- But before choosing which type of exercise is best to do, you need to consult your doctor.
5. Balanced diet
It is recommended to limit the following in your diet:
- foods with added preservatives,
- processed meat in the form of sausages, sausages, bacon, etc.
- smoked meats of any kind,
- products with a long shelf-life;
- foods containing refined sugar;
- alcohol and carbonated drinks;
- canned juice.
Comprehensive diagnosis and treatment will improve the patient’s condition and return them to good health.
FAQs
- What kind of disease can cause pains of an acute, chronic nature, starting in the lumbar region, passing along the leg to the foot?
Spinal stenosis is a chronic pathological process characterized by a decrease (narrowing) in the size of the spinal canal and intervertebral foramen due to the growth of bones and cartilage.
- Can spinal stenosis be cured?
If the spinal canal is less than 1 cm, conservative treatment will not help. Surgery is required in this case of neurological syndromes and absolute stenosis detection. The extreme degree of the disease is when the canal is narrowed to 3 mm – lateral stenosis.
- Can spinal stenosis be treated without surgery?
In the initial stages of the degenerative cascade, the symptoms of spinal stenosis may not be disturbing. However, if the situation worsens, then it is no longer possible to cure the disease without surgery. Removal of stenosis is possible only by surgery.
- What kind of stenosis is dangerous?
Cervical absolute stenosis is the most dangerous since there is a possibility of not the only disability of the patient but death. This is a rare pathology that manifests itself as chest pain, disorders of the genitourinary system, intestines, numbness of the arms and shoulder girdle.
- What happens if the spinal stenosis is not treated?
Spinal stenosis can compress the spinal cord and nerve roots. The lumbar spine is more often affected, less often, the cervical and thoracic. Lack of timely diagnosis and treatment can lead to disruption of the work of internal organs and even disability.














Please, leave your review
Write a comment: