Ball of foot pain or metarsalgia is a biologically important warning signal that indicates foot pathology. Pain in the foot appears as a result of overload, deformation, fractures, pathologies of tendons and joints, or general diseases caused by metabolic disorders. To establish the correct diagnosis, specialists need to know under what circumstances the pain in the foot has occurred. Ball of foot pain can occur due to increased training, improper load distribution, and injuries. In addition, other diseases manifest themselves as pain in the foot but have nothing to do with orthopedics.
The foot consists of 26 bones, which, when connected, form several joints, held together by numerous elastic muscles and strong ligaments. The entire weight of the human body rests on it, so the ball of foot pain causes not only discomfort but, in many cases, limits motor activity.
Varieties of the ball of foot pain
Distinguish by duration:
- Acute pain in the foot – this phenomenon is most often associated with injuries – bone fractures, rupture or sprains, severe bruises.
- Chronic pain that bothers the patient for a long time, in some cases, in the absence of proper treatment, a forced type of gait is formed in a person, which is associated with attempts to maintain the function of movement while sparing the affected limb. The causes of this condition can be both diseases of the foot itself and pathologies of various body systems.
Localization distinguishes:
- Diffuse pain – captures the entire foot.
- Local pain – clearly limited to a specific area.
In some cases, when collecting anamnesis, the doctor suffixes such characteristics of the ball of foot pain, as its location and conditions of occurrence, as well as the presence of concomitant diseases and other symptoms that accompany this pain (numbness of the foot, itching of the skin, etc.). In others, the search for the cause of pain requires a thorough laboratory and instrumental examination.
Ball of foot pain in the early stages
What to do in the early stages of the ball of foot pain?
- See a specialist before the pain in your foot worsens and causes permanent damage.
- Sometimes, to successfully treat a ball of foot pain, it is only necessary to change shoes, reduce the load in the foot, or change the walking technique.
Which doctor should I contact for the ball of foot pain?
Pain in the foot brings significant discomfort and often makes it difficult to move, so you should decide in advance which doctor to contact to avoid standing in lines for a lengthy time and unnecessary trips to the clinic.
- As a rule, an orthopedist deals with the diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation of people with deforming or traumatic damage to bones, joints, muscles, and ligaments of the musculoskeletal system.
- However, patients with diabetes mellitus, first of all, need to make an appointment with an endocrinologist, and if they have vascular problems, go to a phlebologist.
- Rheumatologists treat diseases associated with chronic lesions of the connective tissue. Traumatologist consults patients with foot injuries.
- If symptoms appear that resemble the clinic of an ingrown nail, osteomyelitis, or panaritium, it is necessary to consult a surgeon.
When should you contact a specialist?
- For painful swelling in the foot or ankle, lasting more than five days.
- With open and purulent wounds.
- In the presence of stabbing and cutting pain.
- With repeated complaints.
- If the pain in the foot continues for several weeks in a row.
- In addition to the cramps in the foot, you have a fever.
- With structural changes in the foot, calcaneus, or ankle.
Causes of the ball of foot pain
The main causes are:
- Traumatic injuries to the foot (bruises, sprains, bone fractures). With fractures, the pain is sharp; there is a rapid increase in edema. In many cases, the support function of the foot is lost. Bruises and sprains are characterized by moderate pain, swelling, and bruising. The support is preserved, sometimes limited.
2. The next reason is inflammation affecting the joints of the foot. These include gout, chondrocalcinosis (pseudogout), and rheumatoid types of arthritis.
- Gout is a disease that occurs as a result of a metabolic disorder of uric acid. The deposition of uric acid salts in the joints is called the gouty type of arthritis. Most often, the first metatarsophalangeal joint is affected, which is manifested by a severe attack of pain, redness of this joint, edema, and fever. Usually, an exacerbation of gouty types of arthritis lasts 6-7 days.
- Ball of foot pain can be a symptom of bone pathology. In this case, we can talk about such diseases as osteomyelitis, osteoporosis, bursitis of the metatarsal head, etc.
- Osteomyelitis can result from open fractures, infected wounds, or surgery on the foot. It is manifested by an increase in pain, a deterioration in the general condition; the pain is pulsating, bursting, aggravated by any movement.
- In osteoporosis, due to a decrease in bone density, its strength is impaired. This condition is facilitated by hormonal changes in women during menopause and pregnancy, some endocrine diseases, insufficient intake of calcium and phosphorus from the outside, as well as excessive loads on the musculoskeletal system.
- Bursitis of the heads of the metatarsal bones is a change in the articular capsules of the joints of the foot associated with their increased trauma due to age-related thinning of the fatty layers that protect them. It is manifested by the appearance of painful “bumps” in the projection of the joints of the feet.
- Diseases of the ligamentous apparatus of the foot with pain syndrome include, for example, plantar fasciitis. The calcaneal fascia is a plate of connective tissue that starts at the heel bone and ends at the attachment to the metatarsal heads. With increased loads, overweight, flat feet, the fascia is stretched and injured, which causes inflammation in it. This condition is called plantar fasciitis and is manifested by pain in the instep and on the sides of the foot.
- A condition when the fascia ossifies at the site of its attachment to the heel bone and severe pain in the heel occurs when walking is called a heel spur.
3. The cause of ball of foot pain can be diabetes mellitus, a disease in which the vessels of the microvasculature also suffer due to impaired glucose metabolism.
- Diabetic osteoarthropathy (a type of diabetic foot) predominantly affects the metatarsal parasitic joints. Pain in the feet is initially not intense, but as the pathological process develops, it becomes prolonged, appears even at rest, and a gross deformity of the feet is formed.
- With the neuropathic form of the diabetic foot, zones with hyperkeratosis are formed, painful ulcers and cracks form in their place.
- The ischemic form of the diabetic foot is characterized by a ball of foot pain when walking, persistent swelling of the feet, and weakening of the pulsation of the arteries.
- The diabetic foot with the development of gangrene, along with obliterating atherosclerosis and endarteritis, is one of the most serious complications in diabetes mellitus.
4. Flat feet are characterized by a change in the shape of the arch of the foot, which leads both to a redistribution of the load on the bones and muscles of the foot and to the compression of the vessels and nerves passing through that part of the sole, which normally does not participate in the act of walking. The reasons for the development of flat feet include:
- rickets transferred in childhood;
- wearing improperly selected uncomfortable shoes;
- weightlifting;
- congenital weakness of connective tissue;
- the congenital difference in the length of the legs, etc.
5. Inflammatory processes in the soft tissues of the foot also cause pain. If an infection gets into small wounds during a pedicure or trauma to the skin of the toes, panaritium (purulent inflammation of the periungual tissues) may develop. An ingrown nail (onychocryptosis) is an ingrowth of the nail plate into the lateral edge of the nail fold. This condition is manifested by twitching pain in the affected finger, edema. A complication in the form of infection is possible.
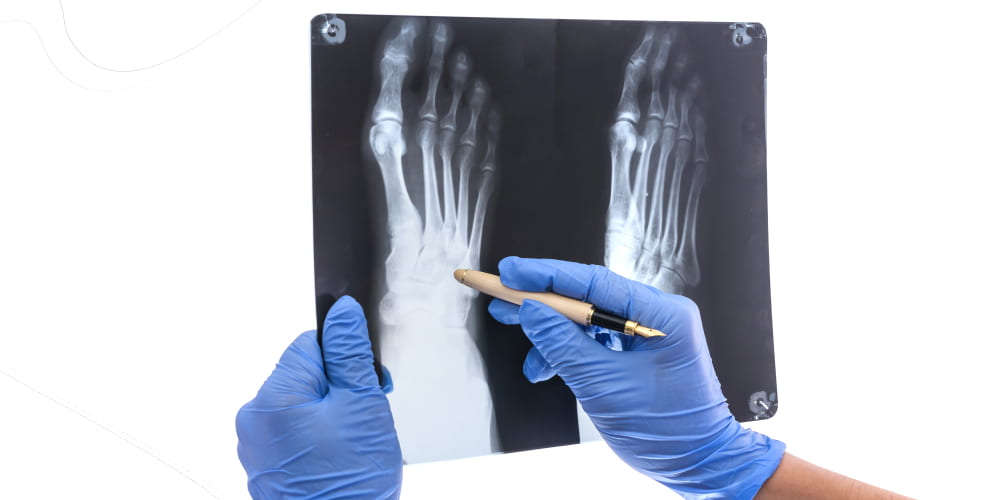
Ball of foot pain diagnostics: instrumental research methods
Diagnostics
Objective examination: palpation of the foot to determine painful areas, the presence of swelling, and foot mobility.
Instrumental research methods
- X-ray of the foot: to exclude pathology of the bones of the foot (fractures, deformities), which can also cause similar symptoms.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT): methods that allow you to image the bones, soft tissues of the foot, tendons, ligaments, and inflammation of the bone structure of the bone itself.
- Ultrasound of soft tissues and joints of the foot and lower leg: localizes the pathological focus both in the joint and outside it. Reveals the presence of excess fluid in the joints of the foot, tendon sheaths. The integrity of the tendons, ligaments, and their functionality.
Ball of foot pain treatment
Finding out the cause of this pathology allows for effective treatment of ball of foot pain.
Pain in the foot can be treated in stages:
- pain in the heels or the Achilles tendon is characteristic of the hindfoot;
- pain in the foot, instep, and internal lateral pain is characteristic of the midfoot;
- pain in the toes, often as a result of transverse flat feet, occurs in the anterior part of the foot.
Elimination of the etiological factor is the most important point in therapy, and often only it is enough to completely relieve pain.
- Traumatic injury and periarticular inflammation require an integrated approach. In addition to analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and local cooling, splints, plaster casts, and special orthoses can be used. Severe injuries require surgical intervention (to restore the integrity of bones, tendons, and ligaments).
- An ingrown toenail, heel spur, and varicose veins that cause ball of foot pain in the right and left foot must be surgically removed. The type and scope of the operation depend on the form and stage of the pathological process.
- Types of arthritis, “diabetic foot”, and gout require systemic supportive therapy, the plan of which must be scheduled by an appropriate specialist. Local treatment without eliminating the cause, in this case, is ineffective.
- Obliterating arterial disease is a complex problem (in terms of a therapeutic approach). To eliminate them, both conservative measures and surgical intervention may be required. Delay can have very serious consequences, sometimes requiring the amputation of a part of the limb.
Ball of foot pain symptomatic therapy, help at home, and prevention
Symptomatic therapy
While doctors are struggling with the cause of the ball of foot pain syndrome, the patient can and should be prescribed symptomatic therapy aimed at reducing it:
- Pain relievers in the form of capsules, tablets, and rectal suppositories. They are prescribed for chronic pain of unexpressed intensity (for long-term use).
- Injectable drugs. More often used in acute conditions.
- Local and regional anesthesia. It is the optimal method of pain relief since it is free from systemic side effects. The use of regional blockages and epidural anesthesia allows the patient to completely get rid of pain.
- Local cold applications, massage, manual therapy, physiotherapy, acupuncture, in most cases, are auxiliary.
A comprehensive examination of the patient is possible (to identify common and rare causes of pain in the foot area). Consultations of narrow specialists, laboratory and instrumental research methods allow us to accurately establish the nature of the pathological process and prescribe an adequate treatment regimen.
Help at home
- Recreation. It is necessary to avoid physical exertion on the lower extremities, especially on the foot, for several days.
- Cold (ice) on the painful area will help reduce pain and swelling.
- Use orthopedic braces to fix the foot.
- Locally on painful areas of the foot, gels and ointments with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (diclac gel, nimid gel, etc.)
Prevention of ball of foot pain
In order to prevent pain in your feet, you should heed these tips:
- Normalization of excess body weight – balanced nutrition, diet.
- Wearing comfortable shoes, orthopedic insoles, bandages.
- Strengthening the muscular-ligamentous apparatus of the foot.
- Prevention of diseases of the joints of the lower extremities and the spine (timely detection of pathology and treatment).
Hopefully, all this information was useful for you. Take care of yourself.
FAQ
- What kind of disease can cause pain in the foot?
Ball of foot pain or metatarsalgia is a biologically important warning signal that indicates foot pathology.
- Why can my foot hurt?
Foot and ankle pain occurs due to injuries, sprains, and fractures. The heel can hurt with plantar fasciitis. In this disease, a strip of tissue along the sole of the foot is damaged. Your feet can hurt from wearing high heels or shoes that are wrong or too tight.
- Does walking barefoot strengthen your feet?
Walking barefoot may also help improve the strength and flexibility of the muscles and ligaments of the foot, which improves the function of the foot, and, therefore, reduces injuries of the foot and improves posture and balance of the body. Walking barefoot on a clean and soft surface is perfectly fine.
- How do you get rid of the ball of your foot?
Grab your toes with one hand and pull them up toward your ankle until you feel a stretch along the bottom of your foot and in your heel cord. Massage the arch of your foot with your other hand during the stretch. Hold for 10 seconds. Repeat 10 times on each foot.
- Why is it painful to step on the heel in the morning?
The main cause of heel pain in the morning is most often due to inflammation of the fascia of the tough connective tissue, due to which a bony growth forms on the heel bone. With bursitis, pain occurs along the edge of the inner side of the foot.
- How can a tennis ball help relieve foot pain?
Another good way to help keep the plantar fascia loose is to roll out along the bottom of the foot. A great way to help loosen up this tissue while simultaneously decreasing pain and inflammation is to roll the bottom of your foot along with a frozen water bottle, lacrosse ball, or tennis ball for 5-10 minutes.
- Why do feet and toes hurt?
Pain in the ball of your foot under the toes and other places can be caused by many different reasons, including injuries, deformations, improper shoes, viruses, and diseases. A common reason is the wrong position of the leg, which leads to a violation of the action of the vector forces falling on it.











Please, leave your review
Write a comment: