Embark on a journey into the sophisticated world of the immune system with this comprehensive overview. It is the body’s formidable defense, safeguarding against pathogens and foreign invaders. Comprising a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs, it orchestrates a coordinated response. It aims to maintain the body’s health and integrity. This guide delves into the immunity’s multifaceted components. They include white blood cells, antibodies, and the lymphatic system. Uncover the sophisticated mechanisms that such a system employs. It will help you to distinguish yourself from non-self, adapt to diverse threats, and form immunological memory. We delve into everything from the first line of defense to the intricacies of adaptive immunity. Our article provides a foundational understanding of the protection system’s remarkable capabilities. Also, it has a pivotal role in sustaining overall well-being. Join us on this illuminating journey into the resilient realm of immunology. We prepare the best overview of the immune system for you.
What is the Immune System?
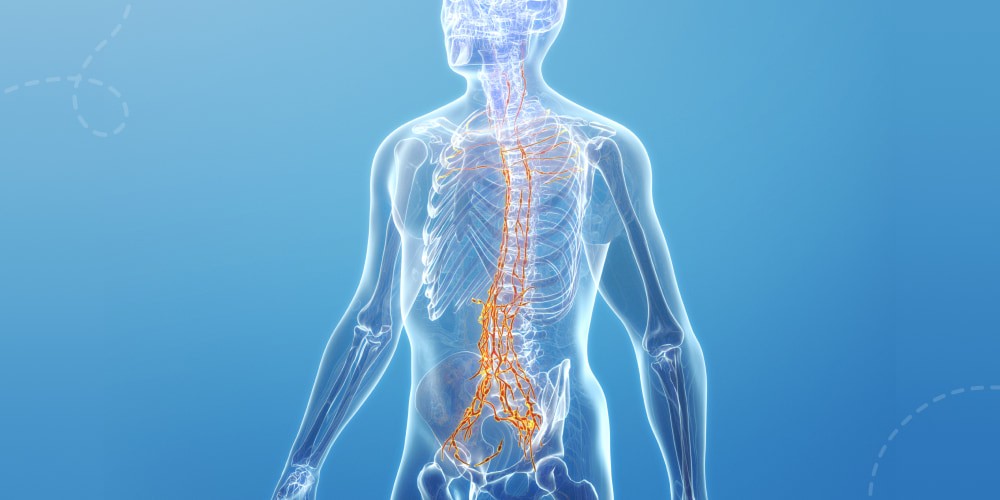
Such a system is a complex and highly sophisticated network of cells, tissues, and organs. They collectively work to defend the body against harmful pathogens. Among them are bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other foreign substances. Its primary function is recognizing and cutting these invaders. It distinguishes them from the body’s cells and tissues. Immunity is pivotal in maintaining overall health and preventing infections. There are critical components of such a system. They include white blood cells, antibodies, lymphatic systems, and signaling molecules. Immunity also has two main branches: the innate resistance system and the innate immune system.
It provides immediate but nonspecific defense mechanisms and an adaptive protection system. It is peculiar and forms immunological memory after exposure to pathogens. Immune can mount rapid responses and adapt to diverse threats. Also, it may remember previous encounters with specific pathogens. It contributes to its effectiveness in safeguarding the body. A balanced immune system is crucial for well-being and protection against various diseases.
The Lymphatic System is an Essential Part of the Immune System
This system plays a multifaceted role in maintaining health. It is necessary to defend the body against infections. Here’s a comprehensive list outlining the essential aspects of the lymphatic system:
- Fluid Circulation: Such a system handles circulating lymph. It is a clear fluid containing white blood cells throughout the body. This fluid originates from the interstitial fluid that bathes the body’s cells and tissues.
- Lymph Nodes: They are strategically located throughout the body. Lymph nodes are critical system components. They filter and trap foreign particles, pathogens, and abnormal cells. Such nodes help their removal from the lymphatic circulation.
- Immune Cell Transport: The lymphatic system is a conduit for immune cells. It is particularly lymphocytes. It allows them to travel to various body parts to detect and combat infections. This cellular transportation contributes to the immune response.
- Fluid Balance: Such a system helps maintain fluid balance within tissues. It absorbs excess interstitial fluid and returns it to the bloodstream. This function prevents the accumulation of fluids in the extracellular spaces.
- Absorption of Dietary Fats: Specialized vessels in the small intestine called lacteals are part of such a system. They absorb dietary fats and fat-soluble vitamins. After, they transport them through the lymphatic vessels before eventually reaching the bloodstream.
- Pathogen Defense: The lymphatic system is critical in the body’s defense against pathogens. Lymph nodes house immune cells that actively identify and attack invading microorganisms. They are preventing the spread of infections.
- Transport of Antigens: This system transports such substances to the lymph nodes. It facilitates the activation of immune cells and the initiation of an adaptive immune response.
- Formation of Lymphocytes: T and B cells are crucial immune system components. The lymphatic system supports these cells’ formation, maturation, and activation. They are essential for an effective immune response.
- Removal of Cellular Debris: This system assists in removing all waste products. This process contributes to tissue repair and regeneration.
- Edema Prevention: Such a system helps prevent edema, a condition characterized by swelling. It does it by maintaining fluid balance and preventing the accumulation of excess fluid in tissues.
The lymphatic system is a dynamic and integral part of the immunity. It orchestrates functions that collectively contribute to the body’s defense against infections. Such a system maintains fluid balance and overall well-being. Its intricate network ensures a harmonious interplay between various immune components. It makes it a cornerstone of the body’s defense mechanisms.
Regulation of the Immune System
The regulation of the immune system is a complex and finely tuned process. That ensures a balanced and effective response to various challenges. Also, it prevents excessive or inappropriate reactions. Several vital mechanisms govern the regulation of immune activities:
- Immunological Tolerance: This system undergoes a process of self-recognition during development. It is learning to distinguish between self and non-self. It induces immunological tolerance, a critical regulatory mechanism. That prevents the immune system from attacking the body’s cells and tissues.
- Cytokine Signaling: It plays a pivotal role in immune regulation. Cytokine signaling modulates the intensity and duration of immune responses. It influences the behavior of immune cells and ensures a controlled reaction to pathogens.
- Checkpoints in Immune Cells: Immune cells, particularly T cells, have checkpoints. They regulate their activation and function. These checkpoints prevent excessive immune responses and help maintain immune homeostasis.
- Suppressor T Cells: Regulatory or suppressor T cells (Tregs) are a specialized subset of T cells. That actively suppresses immune responses. They play a crucial role in preventing autoimmune reactions and maintaining immune tolerance.
- Apoptosis: The immunity employs apoptosis, a process of programmed cell death. It helps to cut unnecessary or potentially harmful immune cells. It helps in fine-tuning the immune response and preventing uncontrolled activation.
- Antigen Presentation: Antigen-presenting cells (APCs) display antigens to T cells, initiating immune responses. Regulation of antigen presentation is necessary to ensure that only appropriate responses work. It avoids unnecessary activation.
- Feedback Inhibition: Harmful feedback mechanisms operate in the immune system. After neutralization, they suppress ongoing immune responses after the threat. It prevents prolonged inflammation and potential damage to healthy tissues.
- Hormonal Regulation: Hormones like cortisol and adrenaline can influence immune responses. The HPA axis and the sympathetic nervous system contribute to hormonal regulation. It modulates immune activities during stress responses.
- Microbiome Interaction: The gut microbiome plays a crucial role in immune regulation. The interaction between the immunity and the body’s diverse microbial communities promotes tolerance.
The regulation of the immune system involves a sophisticated interplay of mechanisms. That balances effective defense and prevention of harmful responses. This intricate regulatory network ensures the system responds to diverse challenges. It avoids detrimental effects on the body’s tissues.
Signs of a Healthy Immune System
Embark on a journey into the indicators of robust immunity with our exploration titled “Signs of a Healthy Immune System.” A well-functioning system is paramount for overall well-being. It acts as the body’s defense against infections and maintains equilibrium. We delve into key markers that signify a robust immune response. Also, we discuss the body’s ability to ward off pathogens to recognize foreign invaders efficiently. We unravel the signs reflecting the immune system’s resilience and vitality. Also, we explore lifestyle factors and holistic well-being as integral components of immune health.
Quick Recovery from Illness
A rapid recovery from illness indicates robust and effective immunity. Several factors contribute to this sign of immune health:
- Efficient Pathogen Recognition: A healthy system promptly recognizes invading pathogens. Among them are viruses or bacteria, triggering an immediate response to neutralize and cut the threat.
- Swift Immune Response: A well-functioning immune system initiates a rapid and coordinated response. It deploys immune cells, antibodies, and other defense mechanisms to target infectious agents.
- Inflammation Regulation: The system swiftly activates inflammation to combat the infection. Also, to regulate it to prevent excessive damage to healthy tissues.
- Antibody Production: Rapid production of antibodies is a crucial aspect of a healthy immune response. Antibodies contribute to the neutralization and elimination of infectious agents.
- Adaptive Immune Memory: A quick recovery often indicates the presence of immunological memory. The adaptive immune system “remembers” previous encounters with specific pathogens. It allows for a faster and more targeted response upon re-exposure.
- Cell-Mediated Immunity: It is crucial in eliminating and containing infected cells.
- Optimal Immune Cell Function: It includes macrophages, neutrophils, and natural killer cells. Such function contributes to the swift identification and elimination of pathogens.
- Healthy Lifestyle Support: Adequate sleep, balanced nutrition, and stress management support immune function. A well-maintained lifestyle enhances the body’s ability to recover quickly from illnesses.
- Viral Clearance: In the case of viral infections, a healthy immune system clears the virus from the body. It leads to a speedy resolution of symptoms.
- Overall Well-Being: Quick recovery is often associated with an individual’s well-being. Good mental and physical health contributes to the resilience of the immunity.
A prompt recovery from illness reflects the system’s effectiveness in combating infections. Also, it suggests a state of immune readiness and adaptability. The speed of recovery is a positive sign. Individuals should rank preventive measures and a healthy lifestyle to maintain immune function.
Consistent Energy Levels
It is a significant indicator of a well-functioning and balanced physiological system. Here, the immune system plays a crucial role. Some aspects highlight the relationship between consistent energy levels and immune health:
- Metabolic Efficiency: A healthy defense system contributes to metabolic efficiency, optimizing energy resources. This efficiency supports overall energy levels throughout the day.
- Reduced Inflammatory Fatigue: It can lead to fatigue. A well-regulated system minimizes unnecessary inflammation. It prevents excessive fatigue and maintains energy balance.
- Effective Nutrient Use: Immunity in harmony helps nutrients are adequate. It ensures that essential vitamins and minerals are available for energy production.
- Balanced Hormonal Response: A well-balanced immune system contributes to a stable hormonal environment. In turn, it supports consistent energy levels.
- Mitochondrial Function: Immune signals affect mitochondria, the energy-producing structures within cells. A healthy system supports optimal mitochondrial function, enhancing cellular energy production.
- Stress Response: Chronic stress can negatively impact the defense system and energy levels. A well-regulated immune response helps modulate the stress response. It prevents excessive energy depletion due to prolonged stress.
- Prevention of Infections: A robust immune system prevents frequent infections that can lead to fatigue. It contributes to sustained energy levels by reducing the burden of illness. This system does it by efficiently combating pathogens.
- Balanced Inflammatory Response: Excessive irritation can contribute to feelings of lethargy and tiredness. A flat inflammatory response helps prevent energy-draining irritation fatigue.
- Quality Sleep Patterns: Immune health interconnects with sleep quality. A well-functioning immune system promotes restorative sleep, restoring energy and daytime alertness.
- Physical and Mental Vitality: A healthy system supports physical and mental vitality. The body can divide energy resources effectively, promoting sustained vigor and mental clarity. It can do it by efficiently managing immune responses.
Consistent energy levels state the absence of immune-related fatigue. They reflect the harmonious interplay between immune function, metabolism, and well-being.
What Vitamins Help the Immune System?
Several vitamins for the immune system help support and enhance immunity’s function. It’s important to note that a balanced and varied diet is the best way to get these minerals for overall health. In some cases, supplementation may be necessary for individuals with specific deficiencies. However, consulting with a healthcare professional before taking supplements is essential. Also, it is vital to maintain a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise and adequate sleep. It helps strengthen immunity. You need to know what vitamins help the immune system.
Vitamin C
Ascorbic acid is a potent antioxidant that helps neutralize free radicals. It protects cells from oxidative stress and damage. Such vitamin is essential for collagen formation. Ascorbic acid contributes to skin health, connective tissues, and blood vessels. It supports the immune system by enhancing the production and function of white blood cells. Vitamin C aids in the body’s defense against infections. It plays a crucial role in wound healing by promoting the synthesis of collagen and facilitating tissue repair. It enables the absorption of non-heme iron from plant-based foods. Ascorbic acid enhances iron use for various physiological functions.
Vitamin D
Calciferol is essential for calcium absorption in the intestines. It promotes bone health and mineralization. Vitamin D regulates calcium and phosphorus levels. It is crucial for maintaining bone density and preventing conditions like osteoporosis. Calciferol acts as an immune system modulator. It influences immune cell function and reduces the risk of autoimmune diseases. Calciferol plays a role in mood regulation and adequate levels with a lower risk of mood disorders. It supports cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis, contributing to overall cellular health.
Conclusion
Everyone needs to know what the immune system is. It is a sophisticated defense network. That safeguards the body against pathogens and maintains overall health. Comprising a complex interplay of cells, tissues, and organs. It orchestrates precise responses to diverse challenges. This system can distinguish self from non-self, adapt, and form immunological memory, which is paramount. Understanding and nurturing the immune system is critical to fostering resilience and well-being. It emphasizes the importance of a holistic approach to health.
FAQ
- When does the immunity become acquired?
The immunity becomes acquired. It develops to confront a specific disease. After vaccination, the immunity also becomes acquired. Acquired immunity is formed throughout life and is a reflection of his individual experience of interaction with environmental antigens.
- What food greatly enhances immunity?
Foods that increase immunity: pumpkin, carrots, beets, tomatoes, garlic, onions, zucchini, herbs, dairy products, citrus, kiwi, strawberry, peach, apple, olive oil, pine nuts, fish, seaweed, and beekeeping derivatives.
- How do lymphocytes destroy foreign cells?
The immune system consists of three types of cells. T-lymphocytes detect a virus or a bacterium in a timely manner. B-cells mark it with antibodies based on a signal from T-lymphocytes. And phagocytes (killer cells), in response to the production of antibodies, destroy a foreign agent.
- What are the humoral factors of the immune system?
Humoral factors of innate immunity are proteins present in blood serum, secretions of mucous membranes, which are synthesized by cells of the immune system and can have a bactericidal, opsonizing, etc., effect on organisms.













Please, leave your review
Write a comment: