Dissecans osteochondritis is a rare diagnosis in patients of all ages. The condition results from the abnormal separation of cartilage from the bone in the joint and can lead to severe pain, swelling, and limited mobility.
In the United States, the overall prevalence of osteochondritis dissecans is not known. However, in the femoral condyles, OCD has a majority of approximately 6 cases per 10,000 men and 3 cases per 10,000 women. OCD occurs in the knee 75% of the time, the elbow 6% of the time, and the ankle 4% of the time.
If you or a loved one are suffering from dissecans osteochondritis, it is vital to seek treatment as soon as possible. Several treatment options are available that can help reduce pain and restore function to the affected joint.
What Are the Types Of Osteochondritis?
Osteochondritis has many types, each with different symptoms and treatment options. Some of the more common types include:
- Osteochondritis dissecans: This type affects the joints, most commonly the knee, elbow, or ankle. It causes pain, stiffness, and deformity.
- Knee osteochondritis: This type affects the knee joint and causes pain and stiffness. It can lead to deformity if left untreated.
- Elbow osteochondritis: This type affects the elbow joint and causes pain, weakness, and deformity.
- Ankle osteochondritis dissecans: This type affects the ankle joint and causes pain, swelling, and deformity.
- Hip osteochondritis: It causes all the same pain and other symptoms as the above diseases.
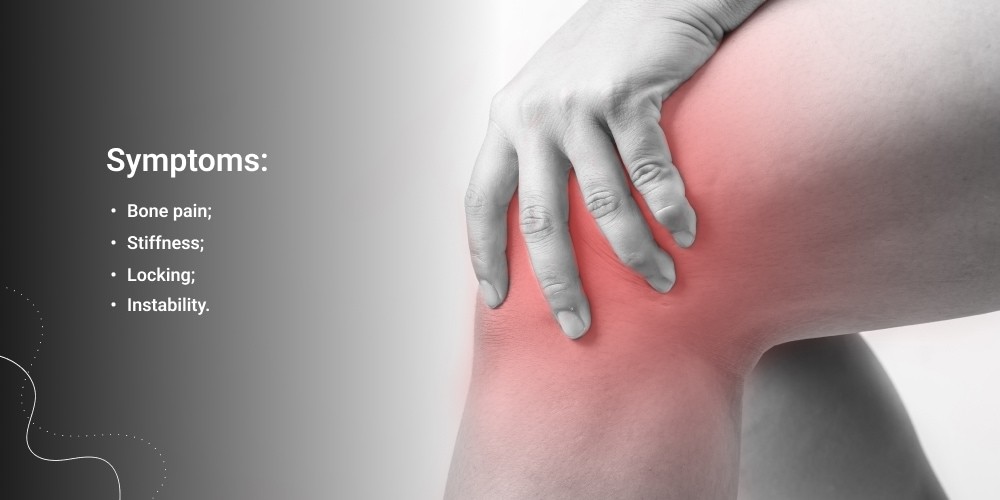
Symptoms of Dissecans Osteochondritis
Osteochondritis dissecans (OCD) is a condition resulting from losing blood supply to the bone. This causes the bone and cartilage to break down. OCD usually affects the knee but can also occur in the elbow, ankle, and shoulder.
Symptoms of osteochondritis dissecans include:
- Bone pain: This is the most common symptom and is typically worse with activity. The pain may be dull or sharp and may radiate from the joint.
- Stiffness: The joint may feel stiff and difficult to move.
- Locking: The joint may lock or pain when trying to bend or straighten it, for example, the knee when you are walking.
- Instability: The joint may feel like it is giving way.
If you have any of these symptoms, visit your doctor. They can perform tests to diagnose OCD. These tests may include X-rays, MRI scans, and CT scans.
Causes of Osteochondritis Dissecans
OCD is caused by the loss of blood supply to the bone. This can happen for many reasons, including:
Causes of osteochondritis dissecans include:
- Trauma: A blow to the affected joint can disrupt blood flow to the cartilage and lead to OD.
- Overuse: Repeated stress on the joints, such as sports, can also disrupt blood flow to the cartilage and lead to OD.
- Anatomical abnormalities: Abnormalities in the shape of the bones or joints can put extra stress on the cartilage and lead to OD.
Osteochondrosis has no single, known cause.
Common factors include stress to the bone, reduced blood supply to the affected area, and trauma to the bone. Osteochondroses can also occur as a result of athletic activity and sports injuries.
Osteochondrosis is almost exclusively found in children and teenagers ages 20. Children who engage in sports are more likely to develop osteochondroses. It’s more common in boys, which may be because boys are at higher risk for injuries than girls.
Risk Factors of Dissecans Osteochondritis
In this block, we will look at the cases in which people can develop this disease.
The following factors may increase your risk of developing OCD:
- Age: OD is more common in adolescents and young adults.
- Gender: OD is more common in boys than girls.
- Joint abnormalities: Abnormalities in the shape of the affected joint can increase the risk of developing OD.
- Family history: Having a family member with OD increases your risk of developing the condition.
Therefore, if you are involved in professional sports, you should stretch your limbs more often, warm them up a lot before training, and properly care for them. In case of an injury, it is your responsibility to provide the correct treatment for the injured limb so that you do not experience further bone problems.
Possible Disease Complications
A medical complication is an adverse outcome of a disease, health condition, or treatment. Complications can adversely affect the prognosis or development of the disease. Among the osteochondritis complications there are:
- Arthritis: The loss of cartilage can lead to arthritis in the affected joint.
- Loose body formation: Dead cartilage can break away from the bone and float around in the joint, causing bone pain and inflammation.
- Joint deformity: The loss of cartilage can cause the bones in the joint to rub against each other, leading to deformity.
Complications can significantly interfere with a healthy and happy life, so they should also be treated. So, to get the right and practical help, you should always consult a doctor. Only a professional doctor can make a correct diagnosis and prescribe appropriate medications.
How to Prevent Osteochondritis Dissecans Ankle?
To prevent this disease, a person must take several necessary steps. These measures are most often associated with the fact that your limb will be limited in movement and unable to function fully for a specific time. In addition, it also includes stretching and other exercises to improve the functioning of your joints. Among the popular methods there are:
- Wearing protective gear for preventing OCD: Wearing knee pads, elbow pads, or other protective equipment can help prevent joint trauma.
- Avoiding overuse: Taking breaks during activities and avoiding repetitive motions can help to prevent overuse injuries.
- Strengthening muscles: Exercising to strengthen the muscles around the joints can help to support them and prevent injury.
N.B. Stretching and similar measures are very useful for those involved in weightlifting or other sports. If you train different muscle groups on different days, it is best to stretch for an hour or 40 minutes during your rest day. If you are engaged in the “full body” complex, you should warm up your joints before each workout and only then start doing sport.
This approach will allow you to maintain the integrity of your joints for many years and give you the chance to progress in your sport. Besides this, stretching is also beneficial for people who prefer an inactive lifestyle and don’t want to get OCD lesions.
How to Treat Dissecans Osteochondritis
The most critical step in any illness is therapy. Only due to appropriate treatment and diagnosis can you recover and feel better. Among the common approaches there are:
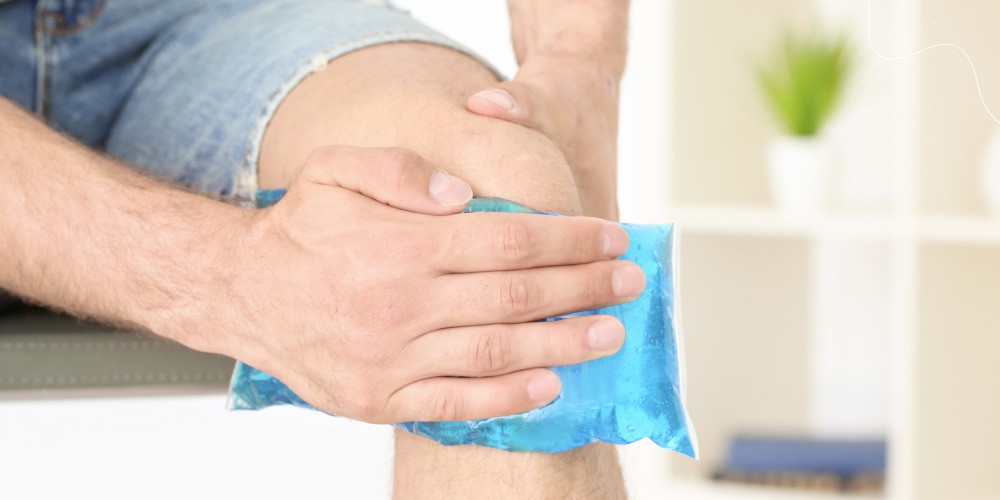
- Rest: Avoiding activities that stress the affected joint can help prevent other OCD lesions.
- Ice: Applying ice to the affected joint can help to reduce pain and swelling. This procedure is similar to a situation when you get your limb punched and need to relieve the pain.
- Physical therapy: Exercises that stretch and strengthen the muscles around the affected joint can help to support it and improve the range of motion. To prevent this disease, you should do some exercises every day.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove dead cartilage or to fuse the bones in the joint together.
Don’t be afraid of doctors; consult your therapist to take the appropriate steps to get well.
Diagnosis of Dissecans Osteochondritis
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. They will also do a physical exam, including an evaluation of the affected joint.
Imaging tests, such as X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans, may be ordered to evaluate the affected joint.
Bottom Line
As you can see, osteochondritis is a rather severe disease that should be treated or prevented. Although its frequency is not as high, this disease can still strongly impact your life.
Prevention is not something difficult to do. And the treatment is not very complicated but can take a lot of time. The most important thing is to choose the proper treatment and preventive measures. And only highly qualified doctors in the field of neurology can do this.
For professional assistance, please call this number 214-619-1910 or use this feedback button. You can fulfill a personal form here if you are a new patient. After you contact us, our managers will provide all the answers to your questions and provide all the necessary instructions for obtaining medical assistance.
Remember that self-care can be dangerous because you don’t know all the human body’s nuances. It’s better to seek help from an experienced team and be happy.
FAQs
- Can osteochondritis dissecans be cured?
Osteochondritis dissecans therapy seeks to restore normal joint function, ease discomfort, and prevent the likelihood of osteoarthritis. There is no single therapy that is effective for everyone. Bone flaws in children’s bones that are still developing mend with rest and care.
- What happens if osteochondritis dissecans are left untreated?
If osteochondritis dissecans is not treated, it can cause cartilage destruction in the joint and loose bone pieces and cartilage to break into the joint. Osteochondritis dissecans, if left untreated, can progress to arthritis. Osteochondritis dissecans most commonly affects the knee, ankle, and elbow joints.
- How do you get rid of osteochondritis dissecans?
By following two approaches:
- Rest your joints. If you have injured your knee, avoid activities that stress your joints, such as jumping or running.
- Physiotherapy. It includes stretching, range of motion, and strengthening exercises for the muscles that support the affected joint.
- Who can have osteochondritis?
Osteochondritis dissecans are more frequent in children and teenagers aged 10 to 20 who are very active in sports.










Please, leave your review
Write a comment: