There’s a reason people say sweets are a great way to cheer yourself up. Sweet foods and sugar raise blood glucose levels. This process improves our mood and gives us a quick energy boost. However, it is important to understand that sugar in our diet can cause several problems. Sugar spikes can cause many health problems. When we eat sweet foods, glucose enters the bloodstream, triggering dopamine release. The process is accompanied by the release of insulin from the pancreas. It’s important to remember that high glucose levels can be harmful to our bodies. This can cause irritability, mood swings, and stress that may lead to depression.
These blood sugar fluctuations negatively affect our brain. These fluctuations begin to affect serotonin levels in the body. Over time, constant sugar consumption leads to repeated blood sugar spikes. These spikes are accompanied by a bad mood, stress, and impaired cognitive activity. It is important to understand the balance between sugar consumption and its impact on health. Moderating sugar intake helps maintain cognitive function. Choosing the right foods is essential for brain health and function.
What Happens to Your Brain During a Sugar Spike
Lone Star Neurology provides effective, high-quality care for patients. For people with neurodegenerative diseases, we offer effective treatment options. You can seek help in cities such as Denton, San Antonio, Carrollton, and others. Excessive sugar consumption is a common health problem today. High sugar intake alters brain chemistry, leading to negative consequences. Sugar spikes significantly impact brain function. Here’s what happens to the brain during sugar spikes:
- A sudden increase in glucose levels. Sugar consumption leads to rapid absorption of glucose from the blood. This process supplies energy to brain cells. The brain recognizes sugar as an immediate energy source.
- Insulin surge. The pancreas produces and releases insulin to help the cells. This process helps brain cells absorb glucose. Insulin helps cells absorb sugar from the bloodstream.
- Dopamine release. Sugar consumption triggers dopamine release, which temporarily boosts energy levels. The brain releases dopamine, creating feelings of pleasure and satisfaction. This makes you feel happy and often crave more sweets.
- Temporary mental activity. One of the main effects is a temporary increase in brain activity. The insulin response helps provide energy to the brain. You may temporarily experience improved memory and focus.
The Insulin Response and Hormonal Imbalance
Contact us with any neurological concerns. Our team is ready to help you. Keep in mind that consuming too much sugar can harm your body. Excessive sugar consumption significantly impacts hormonal balance and increases insulin production. You’ll feel an immediate energy boost, improved mood, and increased activity. While this response helps maintain glucose levels, it can have negative consequences. In response, the pancreas produces more insulin to lower blood glucose. This insulin response can trigger a system-wide hormonal imbalance.
- Fluctuating blood sugar levels trigger cortisol release. Insulin suppresses growth hormone and affects cells. Leptin resistance develops, causing significant appetite regulation problems. Constant sugar consumption increases appetite and stress. This disrupts hormonal balance, leading to neuronal excitability and anxiety.
- Hormonal imbalance causes disruption of the function of brain neurotransmitters. Insulin resistance develops, reducing serotonin synthesis. This makes you more vulnerable to stress and negative emotions. These neurochemical disruptions can have serious effects. Eventually, this may require medical intervention, testing, and treatment.
Mood Swings and Energy Crashes: The Rollercoaster Effect
Mood swings are a common side effect of high sugar consumption. Excess sugar can diminish emotional control and lead to mood instability. Regular sugar consumption creates a cycle of energy surges followed by crashes. Blood glucose levels drop rapidly, triggering stress hormone release. This often leads to irritability, anger, and increased vulnerability to depression.
Energy levels fluctuate due to high sugar consumption. When glucose levels drop, certain areas of the brain can’t function properly. This makes emotional regulation more difficult. Regular sugar consumption repeatedly stimulates dopamine release. This can lead to restlessness, memory problems, and reduced well-being. Frequent mood swings, irritability, and cognitive impairment can result. This process typically manifests as:
- Irritability. When blood sugar drops suddenly, irritability often follows. These blood sugar crashes are particularly problematic when they occur regularly.
- Anxiety. Constant sugar consumption causes increased anxiety. The initial joy and happiness from sugar quickly gives way to unhappiness. This can cause anxiety and sudden mood swings that affect overall health.
- Fatigue. The sudden drop in dopamine levels causes ongoing fatigue. Simple tasks become difficult, and concentration at work suffers. You may find it hard to maintain focus and experience intense sugar cravings.
Cognitive Function and Sugar: Short-Term Boost vs Long-Term Decline
Sugar and cognitive function are closely interconnected. Excessive sugar consumption creates a misleading cycle. At first, dopamine is released, and the person feels good with a surge of energy. However, in the long term, irritability, mood problems, and fatigue develop. Glucose quickly enters the brain, temporarily boosting energy levels. Glucose activates the prefrontal cortex and enhances neural transmission. The brain temporarily receives abundant energy. However, despite temporarily improving alertness, sugar has significant drawbacks. Here are the main ones:
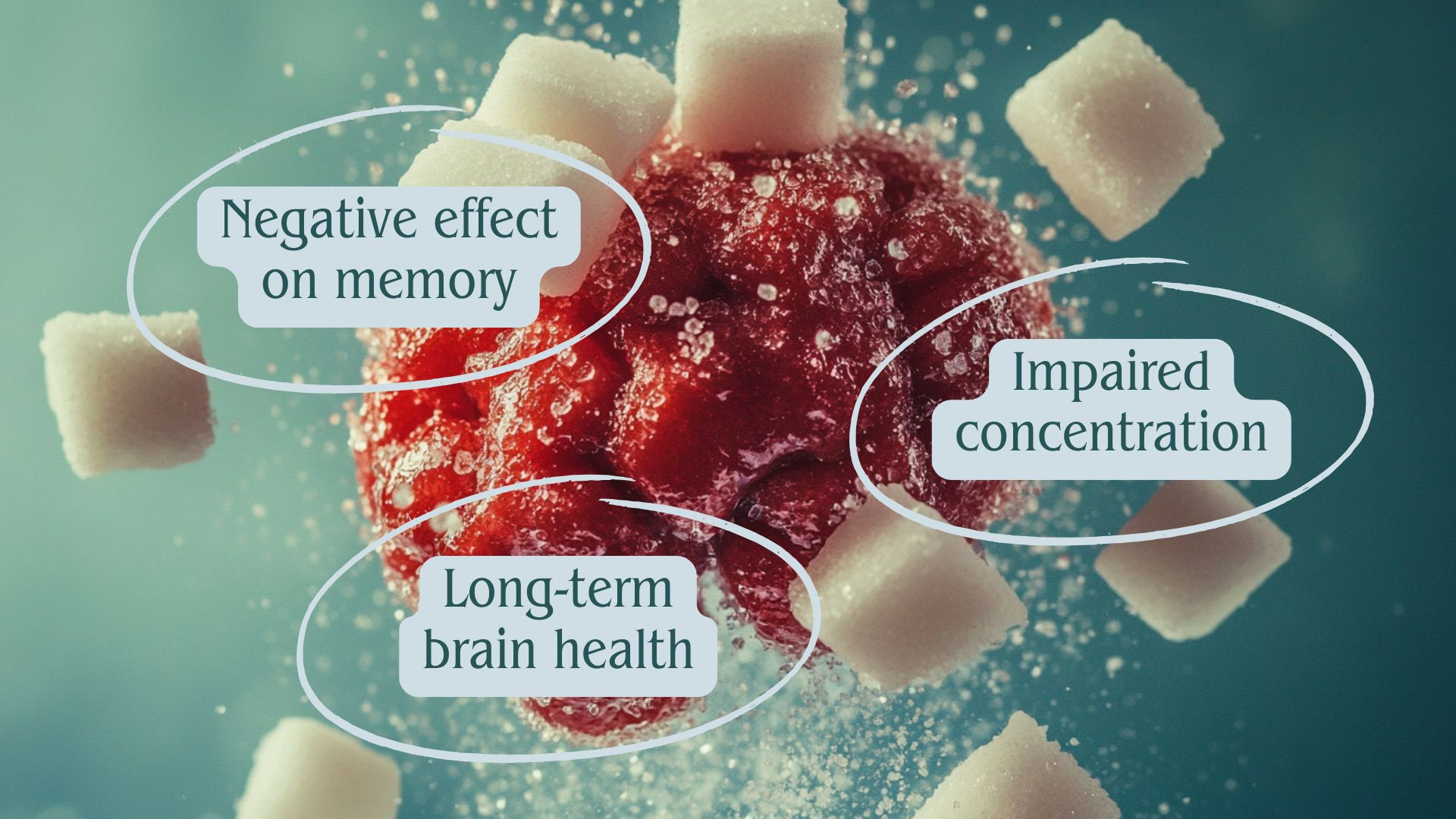
- Negative effect on memory. Consistently high blood sugar decreases important brain growth factors. Over time, cognitive function declines and memory problems develop. Certain brain regions can become damaged, leading to memory impairment.
- Impaired concentration. Excessive blood sugar levels eventually cause an energy deficit in the brain. Sugar impairs neural network function, with significant consequences for brain health. A person begins to have problems with concentration in the long term. This throws off the careful balance of brain chemicals.
- Long-term brain health. Elevated blood sugar accelerates the aging of nerve cells. This increases the risk of neurodegenerative diseases. Serious conditions like neuropathy may develop, requiring treatment. A person may develop Alzheimer’s disease and experience cognitive decline. Repeated sugar spikes can reduce brain volume and impair the formation of new neural connections.
How to Maintain Brain Chemistry Through Balanced Nutrition
Proper nutrition plays a key role in maintaining healthy brain chemistry. Doctors recommend a healthy diet and regular exercise. When blood sugar levels rise, the production of neurotransmitters is disrupted. Eating well is essential for regulating overall health. To increase energy levels and restore strength, a balanced diet is key. Here are some tips for stabilizing blood sugar and reducing disease risk:
- Eating whole foods. Include plenty of vegetables and fruits in your daily diet. Use whole grains, nuts, and seeds. These foods provide steady energy due to their slow digestion. Over time, your blood sugar levels will stabilize, and you’ll feel better.
- Eating protein-rich foods. Include animal protein in your daily meals. Choose fatty fish rich in omega-3s to support brain function. Eat eggs, lean meat, and legumes to regulate mood and avoid sugar spikes.
- Avoiding refined sugar. Avoiding refined sugar is the best way to take care of your health. Avoid white bread, sugary drinks, and pastries in your diet. These foods cause rapid blood sugar spikes that can harm your health. These glucose spikes disrupt brain chemistry, leading to stress and irritability.
LoneStarNeurology helps each patient select a treatment plan. We recommend a nutritious diet to support neurological health. A balanced diet can help improve outcomes and manage neurological conditions.
Why Understanding Sugar’s Role Matters for Mental Health
Sugar consumption directly affects the brain. Blood sugar spikes negatively impact mental health. Your body rapidly responds to changes in blood sugar levels. Fluctuating sugar levels impair concentration. In addition to impaired cognitive function, the work of neurotransmitters deteriorates. The balance of serotonin and dopamine becomes significantly disrupted. High sugar intake also worsens stress responses. This can make you perceive stressors more intensely and have difficulty controlling emotions.
Understanding the relationship between sugar and brain chemistry is important. The negative effects of sugar can contribute to serious neurological conditions. This can contribute to mental health issues and lower self-esteem. Understanding sugar’s effects is the first step toward addressing these problems. Consulting healthcare professionals can help address these negative effects. Start taking care of your health today to avoid mood swings. Remember that you have control over your health choices.









I've given up... the stress her office staff has put me through is just not worth it. You can do so much better, please clean house, either change out your office staff, or find a way for them to be more efficient please. You have to do something. This is not how you want to run your practice. It leaves a very bad impression on your business.
Please, leave your review
Write a comment: