The intestine plays a critical role in supporting overall body health. The intestinal tract has a direct connection with the brain. Disruption of its function has a major impact on brain function and health. The gut microbiome contains billions of bacteria that help the body. Research in this area is advancing rapidly and revealing important insights. This connection is called the gut-brain axis, which affects human health. An imbalance in the intestines can disrupt a person’s nervous system function. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can significantly improve your gut and brain health.
Studies suggest that gut disorders may contribute to the development of Parkinson’s disease or Alzheimer’s disease. Inflammation and gut syndrome are associated with a significant accumulation of plaques in the brain. The brain is responsible for many functions in our body. Disorders in the gut can contribute to neurodegeneration and cause several serious diseases. Early intervention will help determine the cause and prevent the progression of the disease. Doctors will prescribe tests and conduct an examination of the body. A healthy gut is fundamental to overall well being. Intestinal inflammation can contribute to the development of several serious conditions.
The Gut Microbiome and Its Role in Brain Health
Neurologists provide specialized care for people with neurological conditions. Proper medical care can help address these conditions and improve overall health. It’s important to understand that there is a strong connection between the brain and the gut. Intestinal disorders can contribute to several serious health conditions. The gut microbiome includes many trillions of bacteria that live in the digestive tract. They can be found along with viruses and fungi and play a key role in physical and mental health. The gut’s influence on the brain plays a significant role in maintaining good health.
- A healthy gut microbiome positively affects overall health and helps regulate the immune system. Thanks to its action, the body fights against various infections and inflammation. The microbiome helps fight oxidative stress and protect the brain. As a result, the brain functions normally and is resistant to inflammation. The microbiome protects the brain from premature aging and neurodegeneration. This may help reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
- The microbiome produces specific metabolites that affect brain function. Bacteria often synthesize both dopamine and serotonin. These chemicals affect mood, mental activity, and cognitive abilities. The gut microbiome plays a crucial role in regulating brain function. Gut microbes are also involved in the production of fatty acids that have unique properties. They help maintain the barrier and reduce inflammation.
How the Gut-Brain Axis Affects Neurodegeneration
For detailed information about gut-related conditions, it’s important to consult with healthcare professionals. For people with intestinal problems, it is essential to understand what the gut-brain axis is. It is a unique network that connects the central nervous system and the intestinal nervous system. It relies on signals from the immune, hormonal, and neural systems. The gut microbiome has a significant impact on this network. This system can either prevent or contribute to neurodegeneration, depending on its health.
- When this axis functions properly, inflammation is regulated. A healthy balance is maintained in the body’s metabolic processes. This balanced system supports healthy brain function and immune defense. However, problems with the gut-brain axis cause several serious diseases. Often, a person may have dysbiosis or chronic inflammation of the tract. During long-term exposure, anti-inflammatory cytokines are produced and enter the bloodstream. This inflammatory response leads to neuroinflammation and declining health.
- Over time, this can lead to serious mental health problems. Studies have shown that disruptions in this balance contribute to the accumulation of harmful substances. The process is often accompanied by cognitive impairment and various diseases. Increased levels of inflammatory proteins can often be detected in the intestines before they appear in the brain. This process warns of inflammation and adverse effects on the brain. Understanding this mechanism helps guide effective treatment approaches. Early intervention when symptoms appear can lead to more effective treatment.
Inflammation’s Role in Gut Health and Neurodegeneration
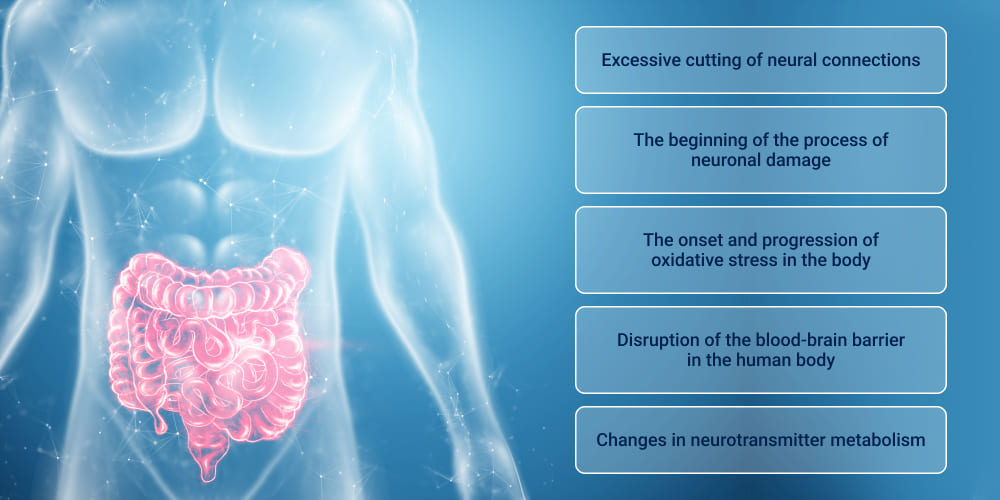
Persistent inflammation is a significant link between the intestinal tract and various diseases. It is usually related to neurodegenerative diseases and causes serious problems. An intestinal disorder can provoke neuroinflammation and worsen the general condition. Dysbiosis can be a big problem for a person. It increases intestinal permeability and harms the body. Various bacteria and viruses penetrate the systemic bloodstream. The process provokes inflammation of a particular barrier and activates immune cells in the brain. Often, a person may experience a deterioration in cognitive abilities and memory loss. Over time, this may increase the person’s risk of developing diseases such as Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s. The main mechanisms of inflammation include:
- Disruption of neural connections.
- The beginning of the process of neuronal damage.
- The onset and progression of oxidative stress in the body.
- Disruption of the blood-brain barrier in the human body.
- Changes in neurotransmitter metabolism.
Disruption of the intestinal microflora provokes serious diseases. The connection between the brain and the gut is integral. Studies have shown that proper nutrition and a special diet can facilitate this process. To reduce inflammation, it is important for a person to consume healthy foods with micronutrients. Omega-3, amino acids, and B vitamins are essential. A good diet full of vitamins strengthens intestinal barriers. Nutrients and vitamins reach the brain and can improve concentration and memory. Short-chain fatty acids help to exert anti-inflammatory effects.
The Impact of Dietary Fiber and Probiotics on Gut Health
Proper nutrition is key to improving gut health. Dietary fiber is one of the best solutions for healthy intestinal metabolism. It has significant neuroprotective potential. Fiber helps the gut produce beneficial short-chain fatty acids. These acids strengthen the intestinal barrier and keep out various bacteria and viruses. They can create a protective barrier that limits the passage of harmful bacteria. Probiotics are another great way to improve overall gut health. They have anti-inflammatory properties and work together with fiber for optimal gut health. A balanced intake of essential fatty acids and vitamins helps improve gut health. Here are the main characteristics of these supplements:
- Dietary fiber. Fibers found in legumes, fruits, and oats promote the development of beneficial probiotic bacteria. These bacteria improve cognitive function and memory. Resistant starches found in foods like cooled potatoes or green bananas can help enhance beneficial gut bacteria. The insoluble fiber found in grains and nuts is essential for cleansing toxins.
- Probiotics. Probiotics are beneficial microorganisms found in fermented foods such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha. They help maintain a healthy gut microbiome by introducing live beneficial bacteria and yeasts. Regular consumption of probiotics can improve digestive health, boost immune function, reduce inflammation, and potentially influence mental health through the gut-brain axis.
The combination of these products has an additional effect on reducing inflammation. The gut microbiome is very sensitive and needs proper care with vitamins and antioxidants. In the early stages of the disease, these elements will help reduce inflammation.
How Mental Health and Gut Health Are Linked
Mental health is closely related to gut health. The gut is directly connected to the brain through cognitive and emotional centers. This complex system functions optimally when properly cared for. Gut microbes have strong connections to various brain systems. Gut bacteria have a significant impact on human health. These gut bacteria affect the emotional state through several main mechanisms:
- The effect on mental health is manifested through the production of neurotransmitters. It is known that gut microbes synthesize serotonin with dopamine. Neurotransmitters are central to the regulation of our mood and memory.
- Neural communication between gut bacteria and the brain is essential. It affects emotional processing and mood regulation.
- Another mechanism is immune regulation, where the microbiome shapes inflammatory responses.
- Bacterial metabolites affect brain health and function.
People with anxiety and depression often have gut microbiome disorders. This can lead to inflammation and increase the risk of serious diseases. People with anxiety and depression often show decreased gut microbial diversity. They often have an increased number of anti-inflammatory bacteria. Another demonstration is the change in bacterial metabolites.
Addressing gut health is an essential component of improving mental health. Special medications, diets, and healthy sleep play a key role. Reducing stress can also help improve health. Researchers have observed positive changes in people who maintain healthy dietary habits.
How to Improve Gut Health for Brain Protection
There are several ways to improve gut function. The gut plays a vital role in the maintenance and long-term function of the brain. Specific dietary and lifestyle strategies can help create an effective treatment plan. Focusing on diet, lifestyle changes, and the right supplements will help with this. The gut microbiome contains many different beneficial bacteria. Here are a few ways to keep your gut healthy for further brain health:
- Dietary changes. Increasing dietary fiber intake is a key first step toward better gut health. Add vegetables, fruits, legumes, and whole grains to your diet. Fermented foods will also help introduce beneficial live bacteria. Consume fermented foods like kefir and sauerkraut, which are particularly beneficial. Berries and dark chocolate support beneficial intestinal bacteria. Reducing processed foods, alcohol, and sugar will help maintain gut health. Intermittent fasting will also help you stay healthy.
- Adding probiotics. Add inulin and omega-3 fatty acids to your diet. They will help reduce intestinal inflammation and maintain membrane integrity. Don’t forget vitamin D, which is important for immune system function.
Lifestyle adjustments. Stress management practices are essential for health. Exercise and good sleep will ensure mental health. Minimizing exposure to environmental toxins is another important step toward better health.








Please, leave your review
Write a comment: